4. DNA-protein complexes
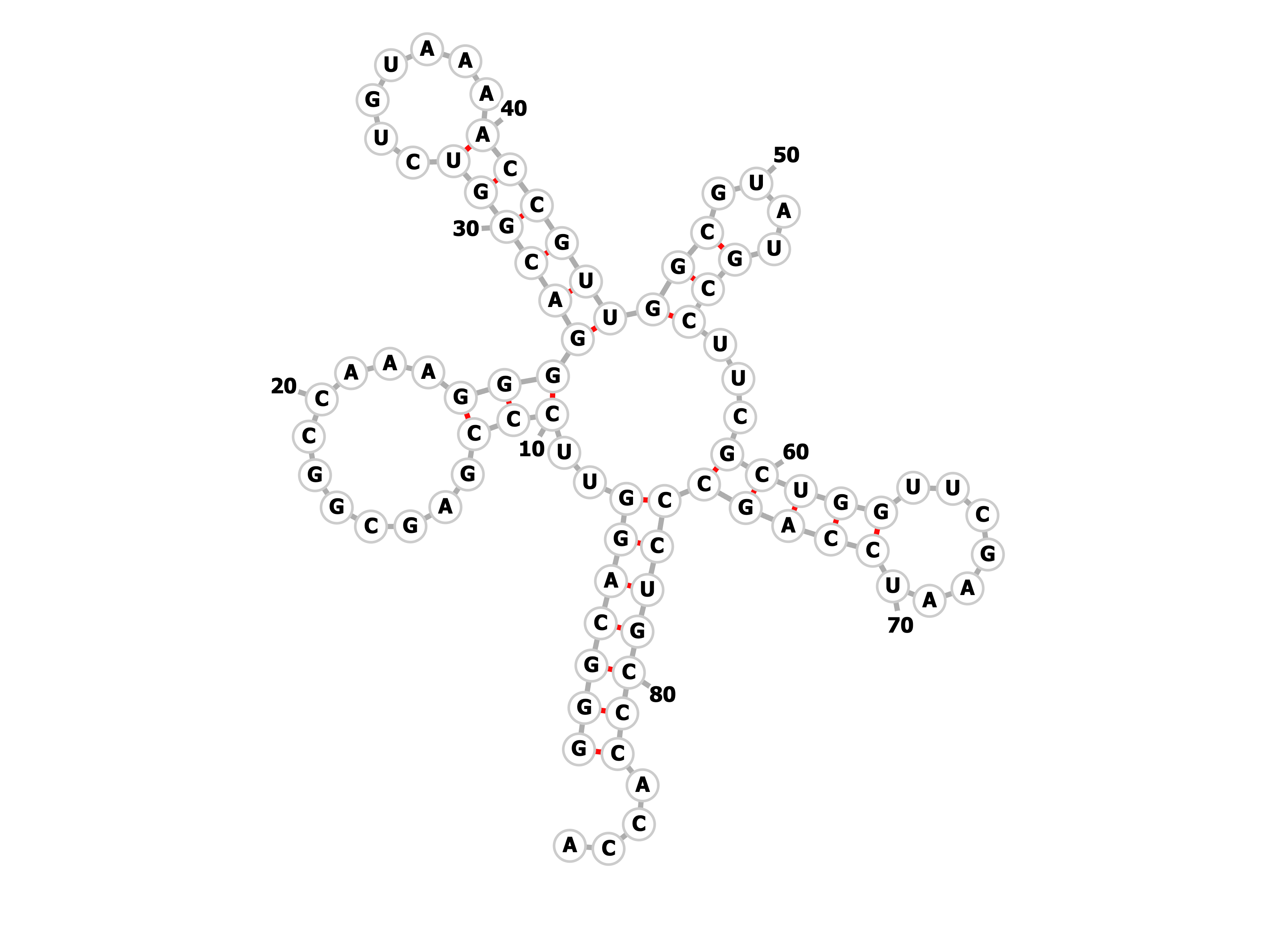
Task1. Predicting of secondary structure of the given tRNA.
Using einverted command inverted sections of nucleotide sequences was found. Given options:
-gap 12 -threshold 0 -match 3 -mismatch -3
Even with these options only acceptor stem was found.

| Structure type | Positions in the structure (find_pair result) | Positions in the structure (einverted result) | Positions in the structure (Zucker's algorithm result) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acceptor stem | 1-7 : 66-72 | 1-7 : 76-82 | 1-7 : 76-82 |
| D-stem | 10-14 : 21-25 | - | 10-12 : 24-26 |
| T-stem | 49-53 : 61-65 | - | 46-48 : 53-55 |
| Anticodon stem | 39-44 : 26-31 | - | 40-45 : 27-32 |
| Total number of canonical base pairs | 34 | 7 | 24 |
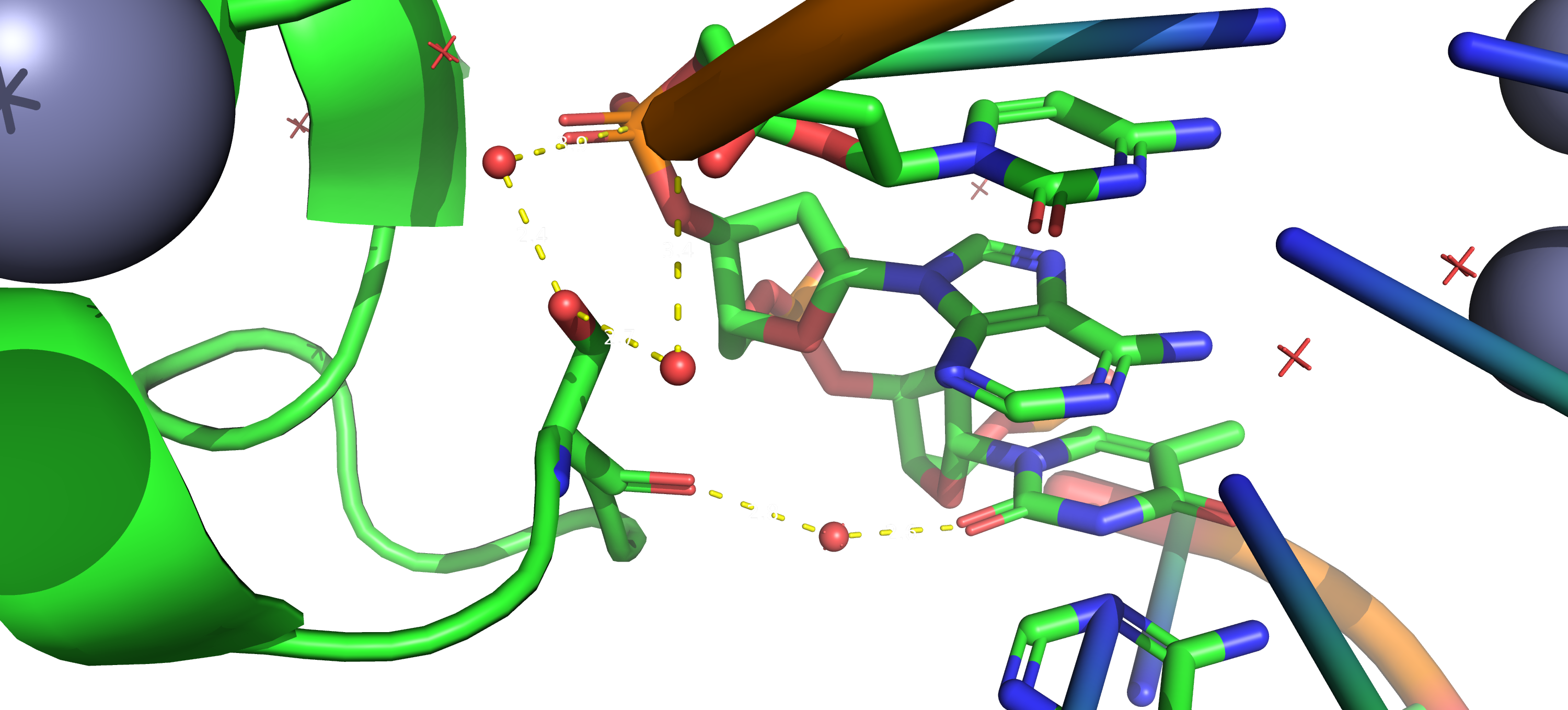
Task 2.1. Searching for DNA-protein contacts in the given structure.
A DNA-protein comlex (PDB ID: 1pp7) was taken for analysis. A script was written to
hilight the following structures:
set 1 - set of oxygen atoms of 2'-deoxyribose
set 2 - set of oxygen atoms in the phosphoric acid residue
set 3 - set of nitrogen atoms in nitrogenous bases
Download this script from this link.
In addition, another script was written for Pymol, the call of which gives a sequential image of the entire structure, only DNA in a ribbon model, the same model, but with a set of set1, then set2 and set3 atoms highlighted in spheres. You can download this script from this link.
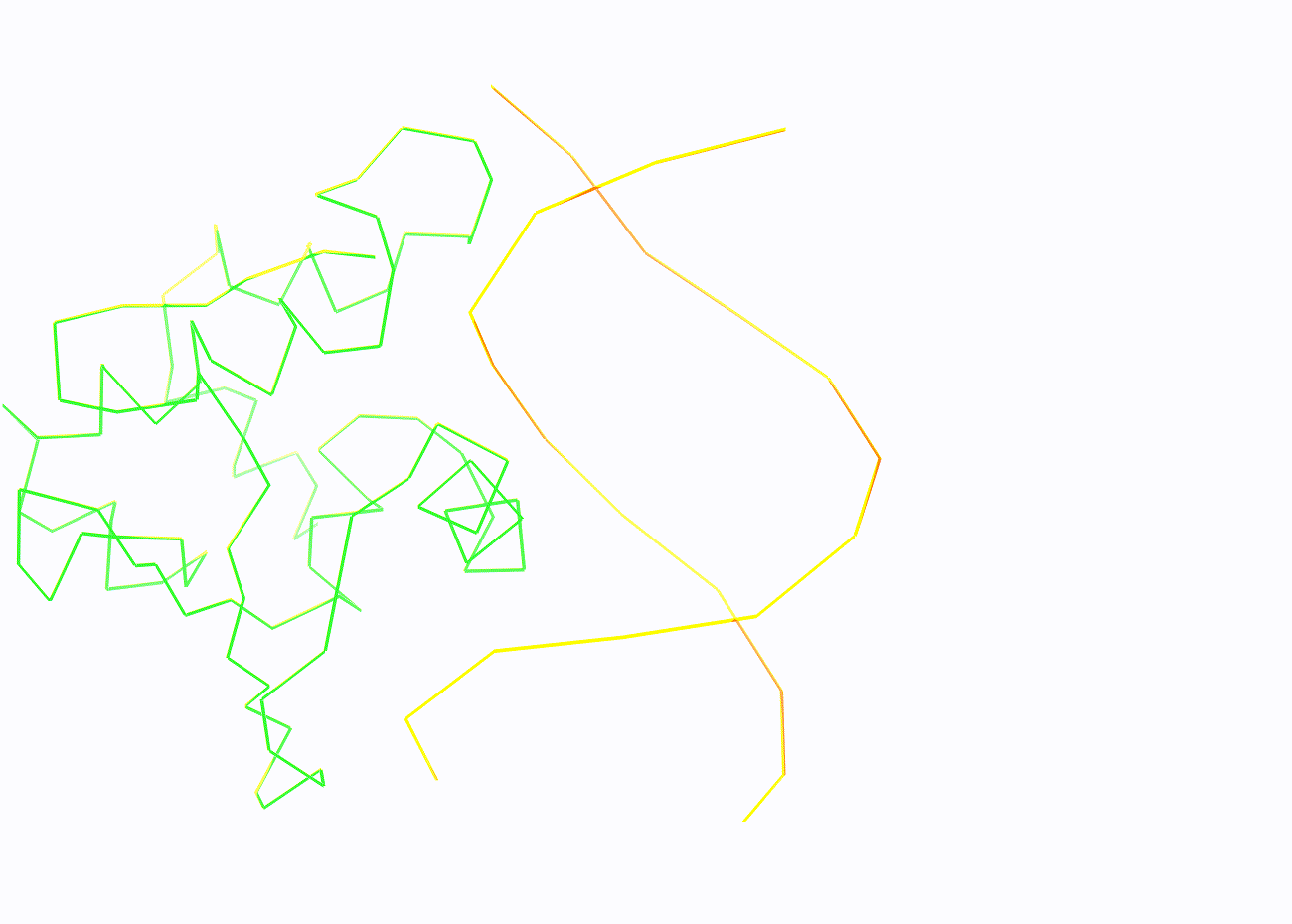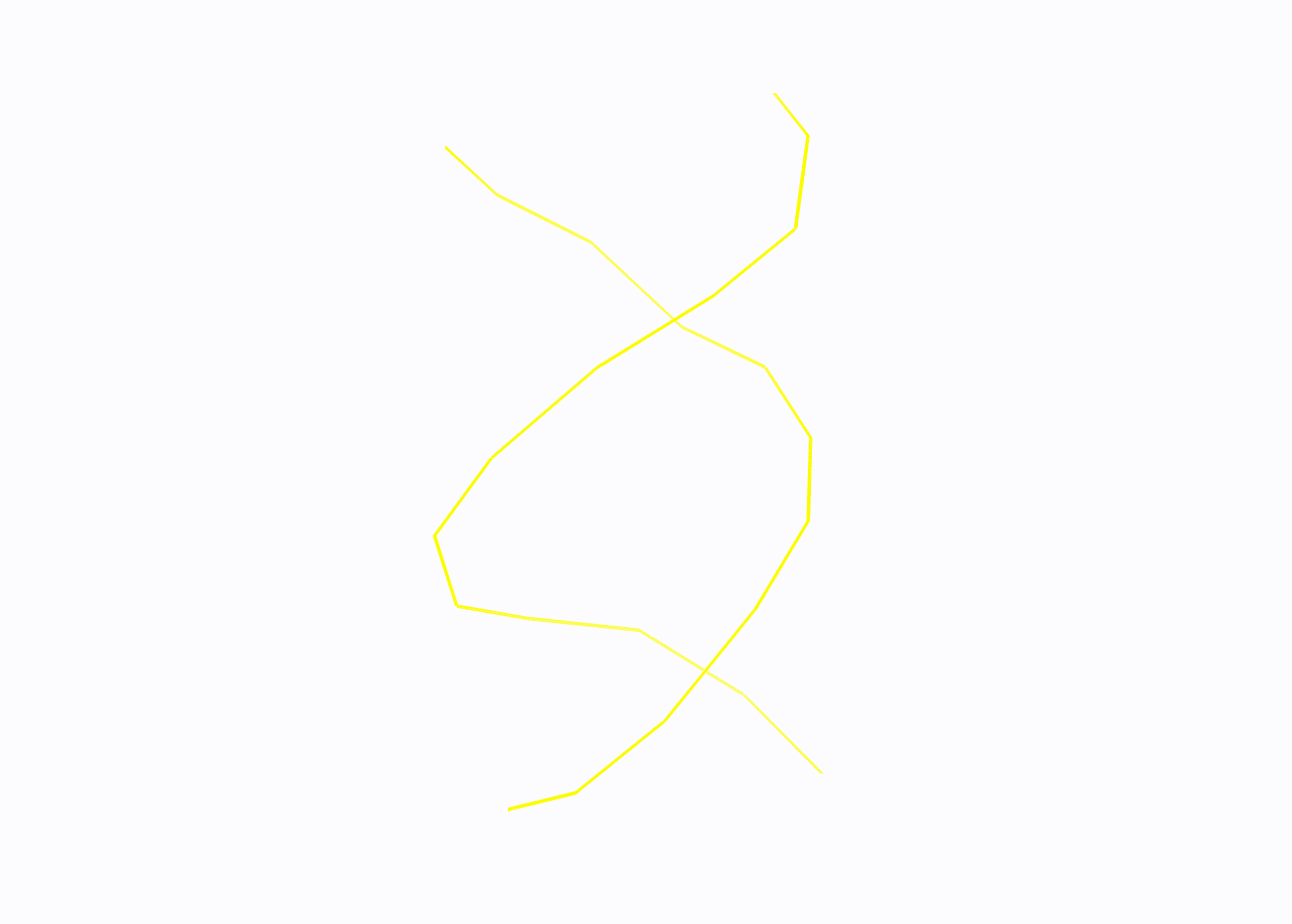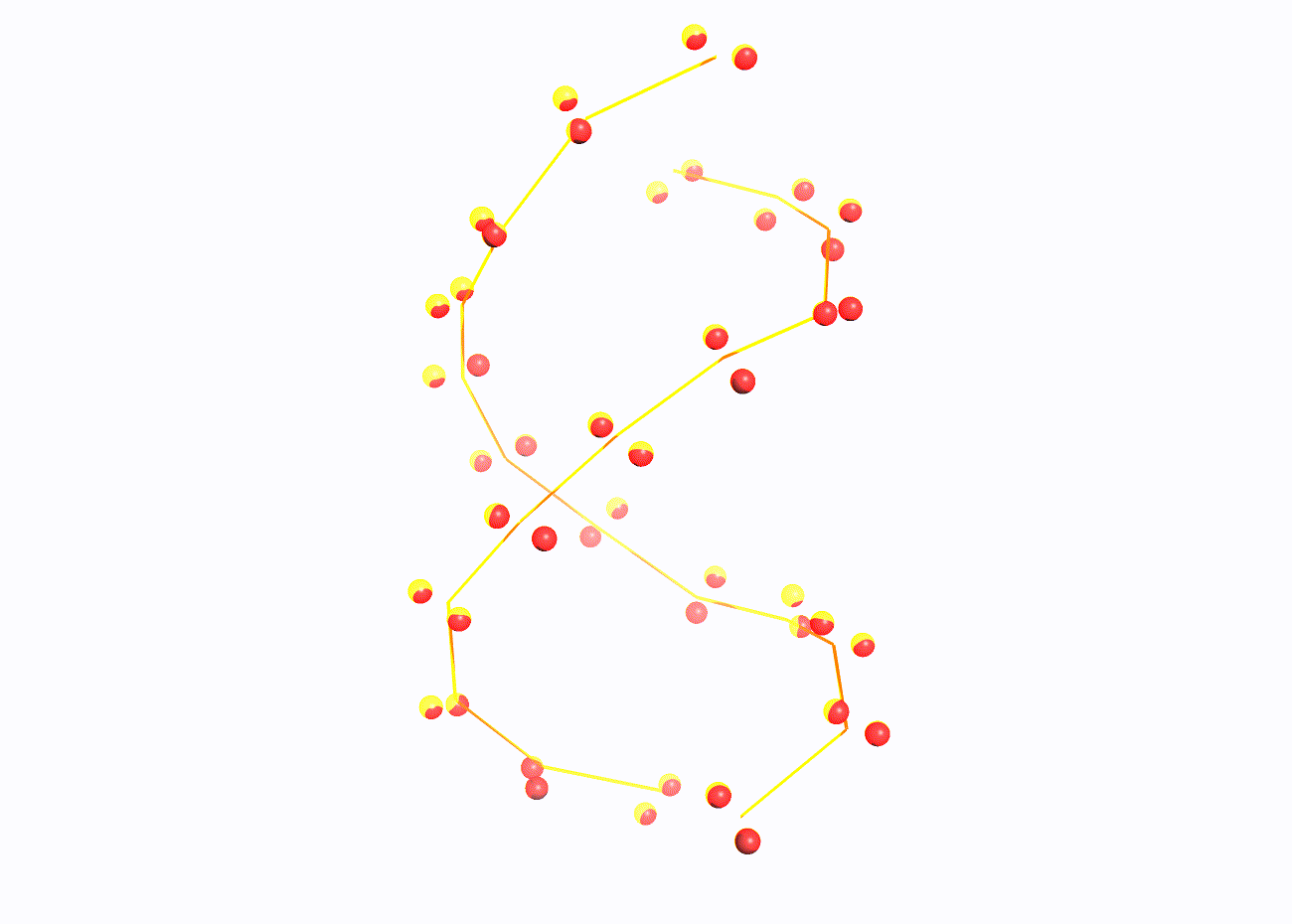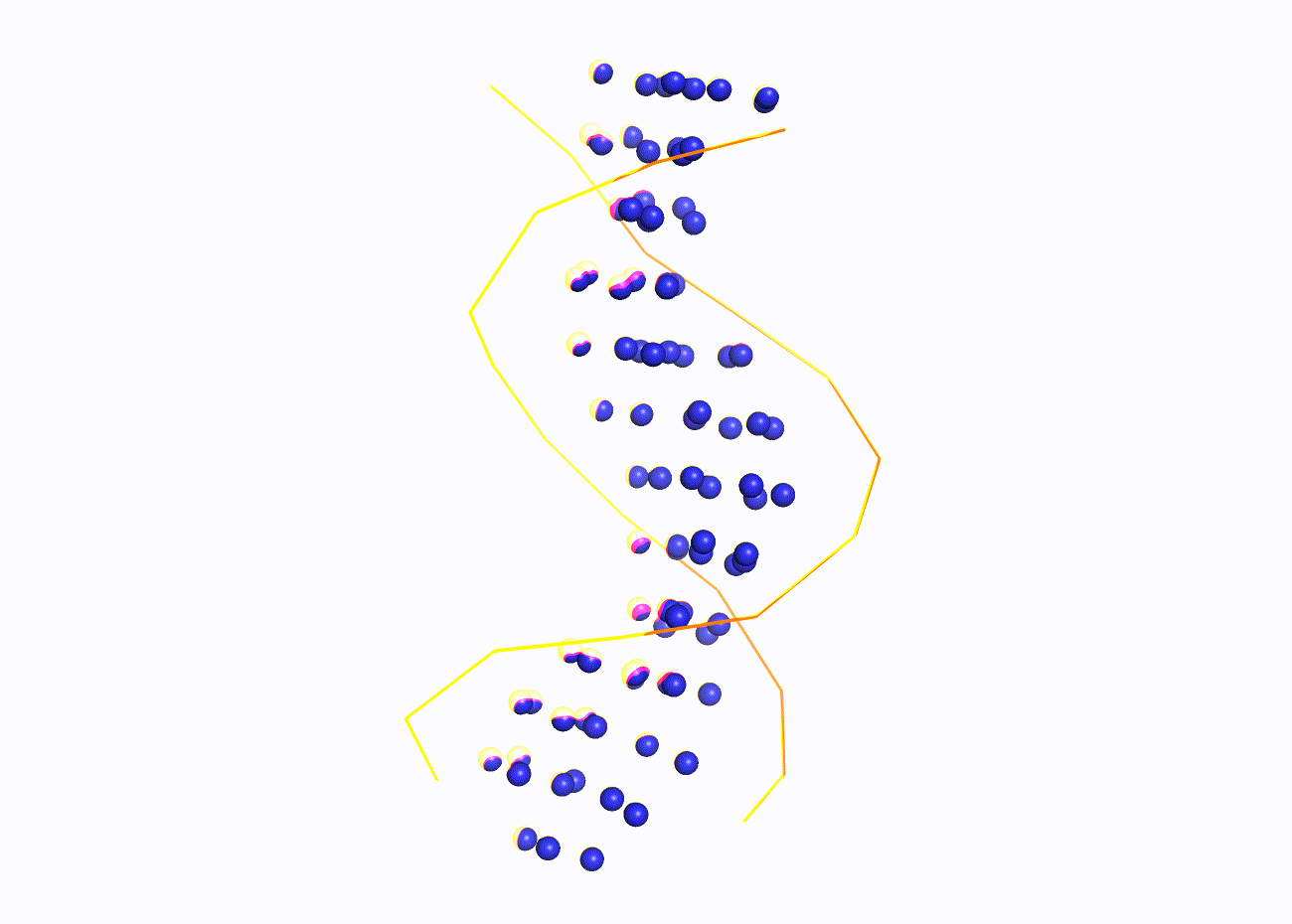
Task 2.2
| Contacts of protein atoms with: | Polar | Non-polar | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2'-deoxyribose residues | 5 | 23 | 28 |
| Phosphoric acid residues | 9 | 34 | 43 |
| Residues of nitrogenous bases on the side of the major groove | 2 | 7 | 9 |
| Residues of nitrogenous bases on the side of the minor groove | 2 | 1 | 3 |
From the data obtained, we can conclude that the protein interacts mainly nonspecifically with the backbone, but there are also contacts with nitrogenous bases in both grooves (especially in the major groove).
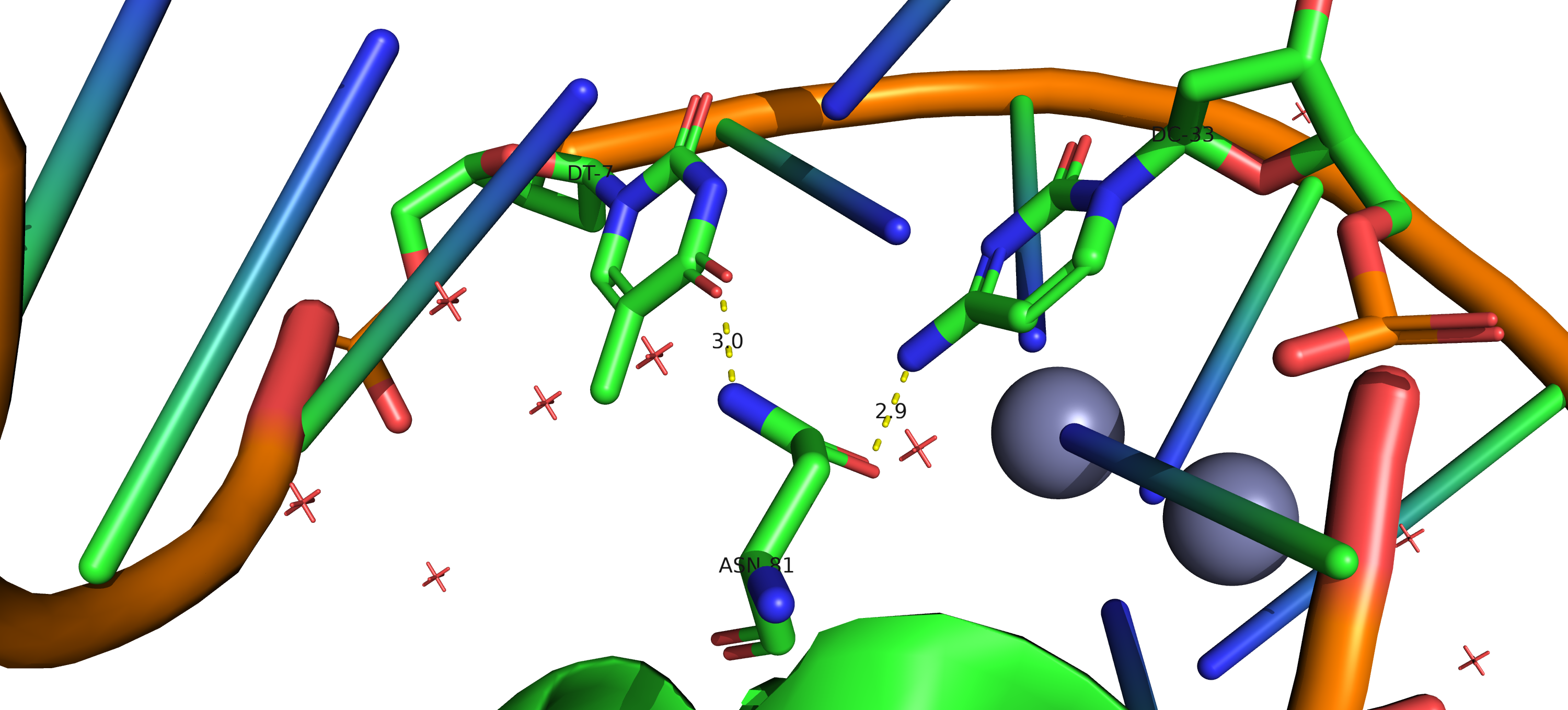
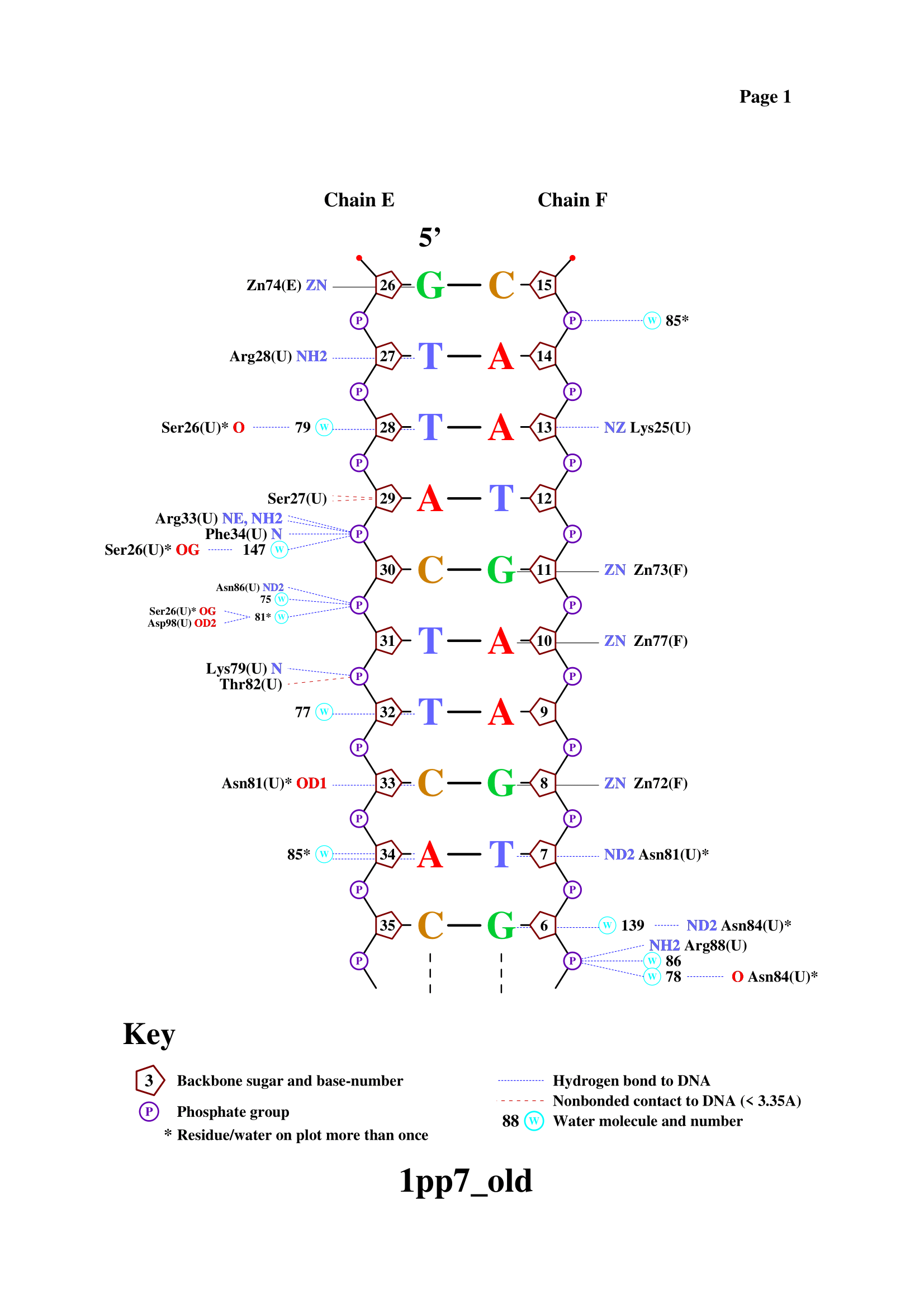
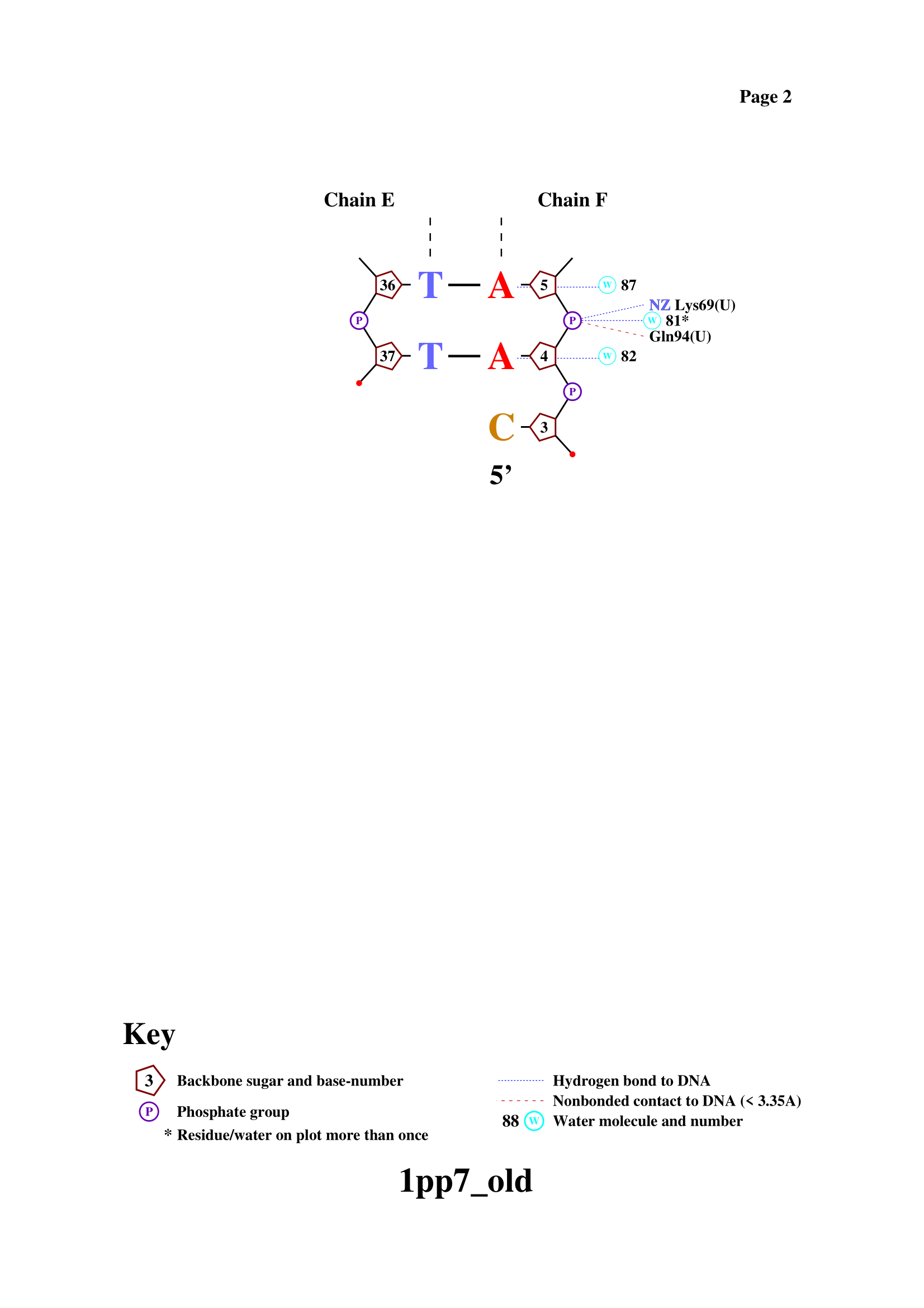
Task 2.3 - 2.4. DNA-protein contacts using nucplot
Using nucplot, file with DNA-protein contacts was obtained.
As it expected, most contacts occur with sugar-phosphate backbone. Serin 26 has largest number of contacts according to the scheme. All of them through water bridges: two with sugar-phosphate backbone, one - with nitrogenous base. Asparagine 81 residue is the most important for DNA sequence recognition. It has two contacts with nitrogenous bases (one on each DNA strand).