MAIN
TERMS
PROJECTS
ABOUT
Prediction of tRNA secondary structure
"einverted"
with defaults didn't show any inverted patterns, so it was decided to run a program with gap penalty [4] and Minimum score
threshold [10]. That run showed one inverted pattern, presented below.
SEQUENCE: Score 21: 7/7 (100%) matches, 0 gaps
1 cggggag 7
|||||||
73 gcccctc 67
SEQUENCE: Score 21: 7/7 (100%) matches, 0 gaps 1 cggggag 7 ||||||| 73 gcccctc 67
Zuker algorithm
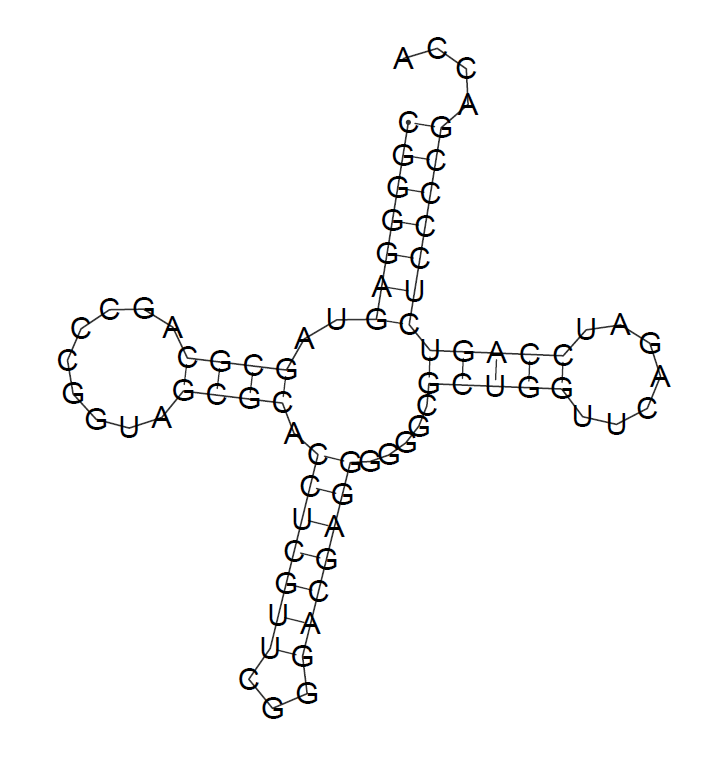
Predicted structure
| Stem | find_pair results | einverted results | RNAfold results |
| Acceptor stem | 5'-4-7-3' 5'-66-69-3' 4 pairs |
5'-1-7-3' 5'-66-72-3' 7 pairs |
5'-1-7-3' 5'-66-72-3' 7 pairs |
| T-stem | 5'-49-53-3' 5'-61-65-3' 5 pairs |
- | 5'-49-53-3' 5'-61-65-3' 4 pairs |
| Anticodon stem | 5'-26-32-3' 5'-38-44-3' 7 pairs |
- | 5'-27-33-3' 5'-37-43-3' 7 pairs |
| D-stem | 5'-10-13-3' 5'-23-26-3' 4 pairs |
- | 5'-10-13-3' 5'-23-26-3' 4 pairs |
| Amount of Watson-Crick base pairs | 19 | 7 pairs | 22 pairs |
Here we can see that real secondary structure is quite similar to the RNAfold result.
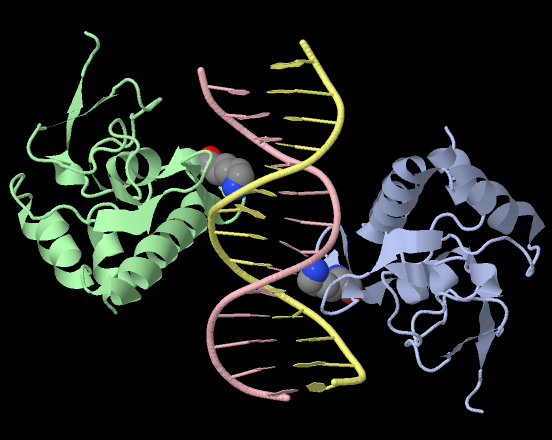
DNA-protein contacts
Jmol commands for definition atom groups are presented below.
define set1 (:D.O4' or :D.O3' or :D.O5' or :C.O4' or :C.O3' or :C.O5')
define set2 (:C.OP2, :C.OP1, :D.OP2, :D.OP1)
define set3 nitrogen and dna
script1
script2
Different types of contacts in 1mhd.pdb complex
| Contacts with: | Polar | Nonpolar | Total |
| 2'-deoxyribose residues | 1 contacts | 9 contacts | 10 contacts |
| phosphoric acid residues | 9 contacts | 2 contacts | 11 contacts |
| nitrogenous bases residues (major groove) | 8 contacts | 6 contacts | 14 contacts |
| nitrogenous bases residues (minor groove) | 0 contacts | 0 contacts | 0 contacts |
Here we can see that the highest number of contacts is shown for contacts with nitrogenous bases residues in the major groove. It must be caused by the large size of nitrogenous bases and it's big potential to form contacts due to their electrochemical structure.
nucplot
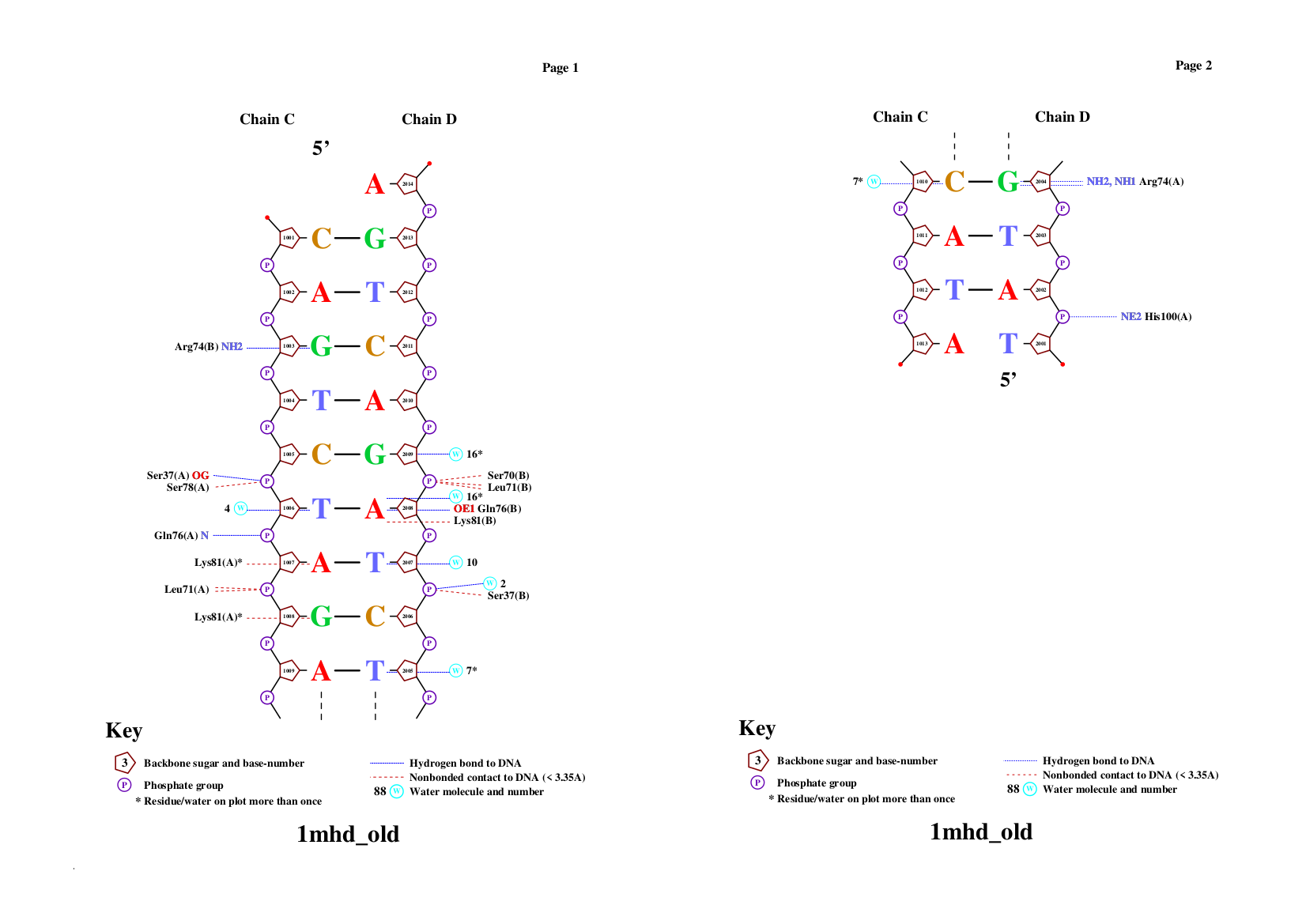
nucplot output
The output shows that the residues with the highest number of contacts(3) are Lys81A and Lys81B. So those residues must be the most important for identification. (If point mutation will suddenly happens, the conformation change will be more critical)
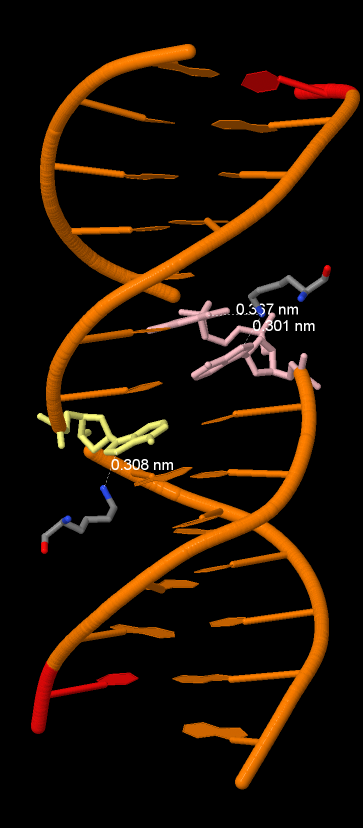
Aminoacid residues Lys81A and Lys81B and their iteractions with DNA