Nucleotide BLAST
Function of a sequence
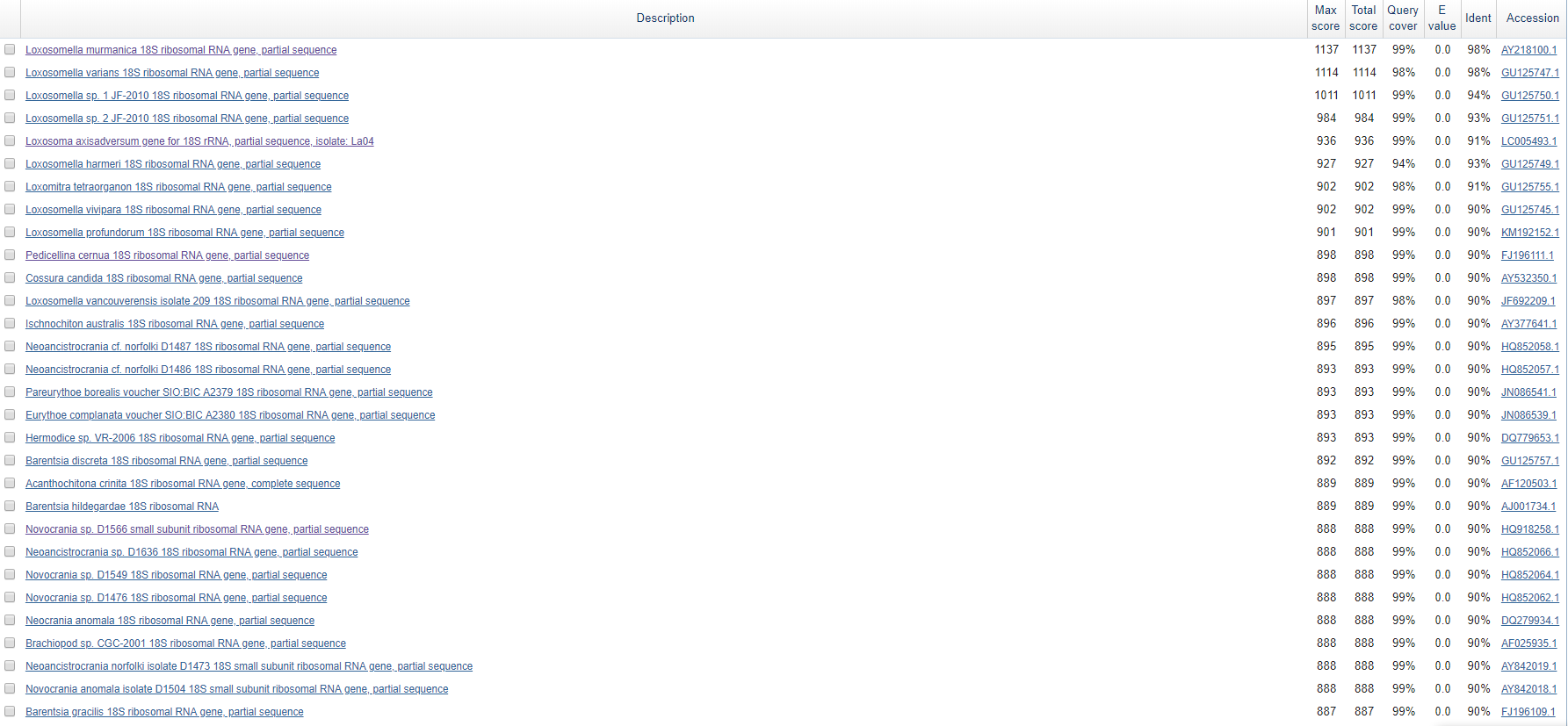
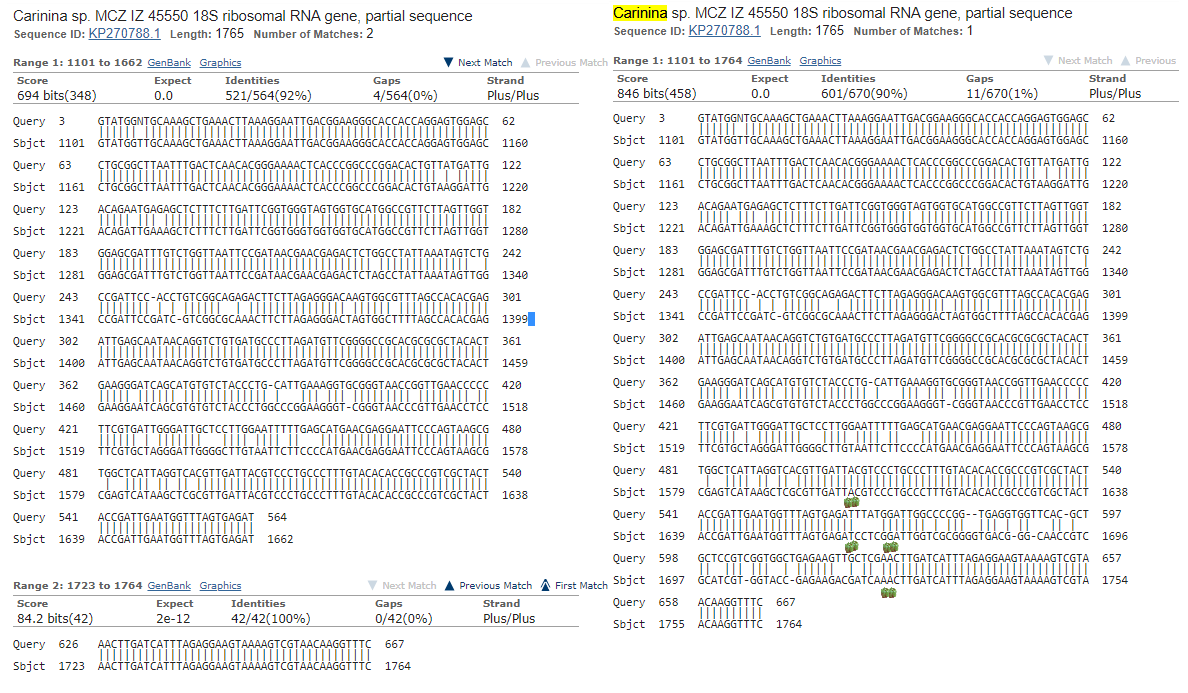
Higher the table of alignments is presented. We can see, that all of the alignments are correspond to 18S ribosomal RNA gene, so we can say with certainty that given sequence must be a 18S rRNA gene sequence.
Predicted taxonomy
To predict the taxonomy of an organism, it was decided to investigate a multiple alignment of a sequences. We can see, that first top-4 of an alignments correspond to be a different species of Loxosomella
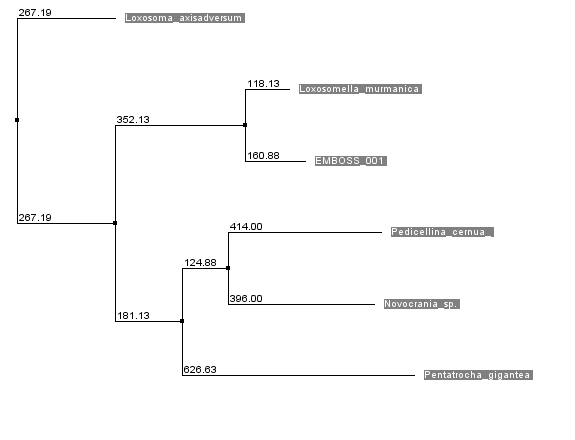
To validate our prediction, it was decided to make a multiple alignment of different findings from a result. The part of that alignment is presented below.
It seems that all sequences are quite similar, and that fact accords with the fact, that 18S rRNA gene is quite conserved. But we can see, that between Loxosomella murmanica and our sequences,
there are more similarities, neither between other species. The same result occurs, when analysis of phylogenetic tree is performed.
So, we can see, that computational data corresponds us, that our sequence is from Loxosomella murmanica, genus Loxosomella, family Loxosomatidae, phylum Entoprocta. The most similar alignment (Loxosoma)
from the same family(according to WoRMS database)
are unexpectedly placed as an outgroup, according to filogenetical analysis. Loxosomella murmanica picture is presented below.
Comparison of findings
To compare different search algorithms, it was decided, at first, to run Megablast with defaults, BLASTN with defaults, and BLASTN with word size 11. All runs were limitate with 10000 hitlist size.
But this comparison didn't show any significant and interpretable result: all of the results were 10000 alignments length, so it seems, that they were limitate by our hitlist size, neither than the
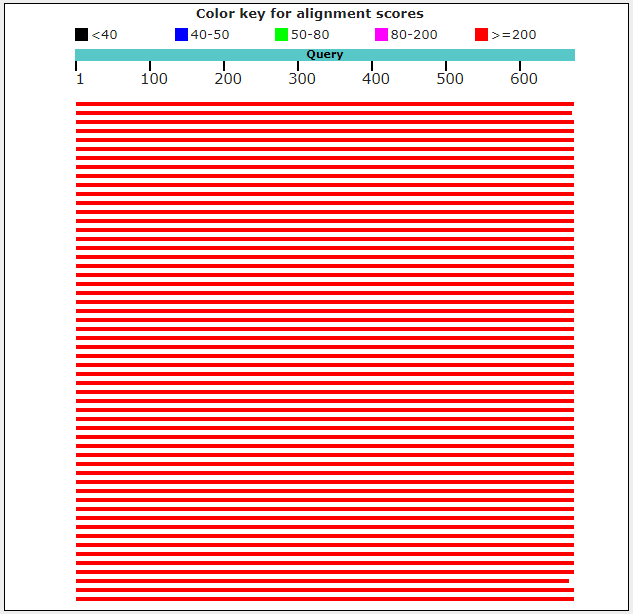
total amount of alignments. Also, all of the e-values were 0.0 points exactly, except the last alignment in megablast result (picture below). It looks quite overwhelmed, because a lot of the sequences
in alignments were from very different taxonomical groups, even from different phylums (for example, the last result in megablast alignments was Aneboconcha obscura from Brachiopoda phylum,
and the last but one result was Miobantia fuscata from Arthropoda phylum), but all of that findings have high statistical significance (= low e-value). It must be caused by the fact,
that 18S rRNA genes are usually conservative in different species.

To get more interesting and significant results, it was decided to run the same BLAST algorithms with different parameters and exclusions. At first, Loxosomatidae family was excluded from search,
and also search was limited with Metazoa taxon. Also, 1000 hitlist size was selected. In 1000 alignments of all algorithms, all e-values were 0.0. The last finding in all algorithms was the same
(Salvatoria clavata 18S ribosomal RNA gene), but Megablast algorithm gives the lower max and total scores for it (776 points) than both blastn algorithms(820). It must be a result of more qualitative
search of megablast, that algorithm works with more similar sequences, and to less similar sequences it gives fewer scores. Also, it was decided to run both algorithms with Match/Mismatch scores 1;-4 and
the same limitations, as in the previous run. And here quite more interesting result appears. At first, e-values at that 3 runs were differed from 0.0 as in previous runs. Usually, for megablast alignments,
they were lower. Also, in BLASTN there were alignments, especially at the bottom of the table, that megablast didn't found (Nierstraszella lineata 18S rRNA gene), and that also must be a result of
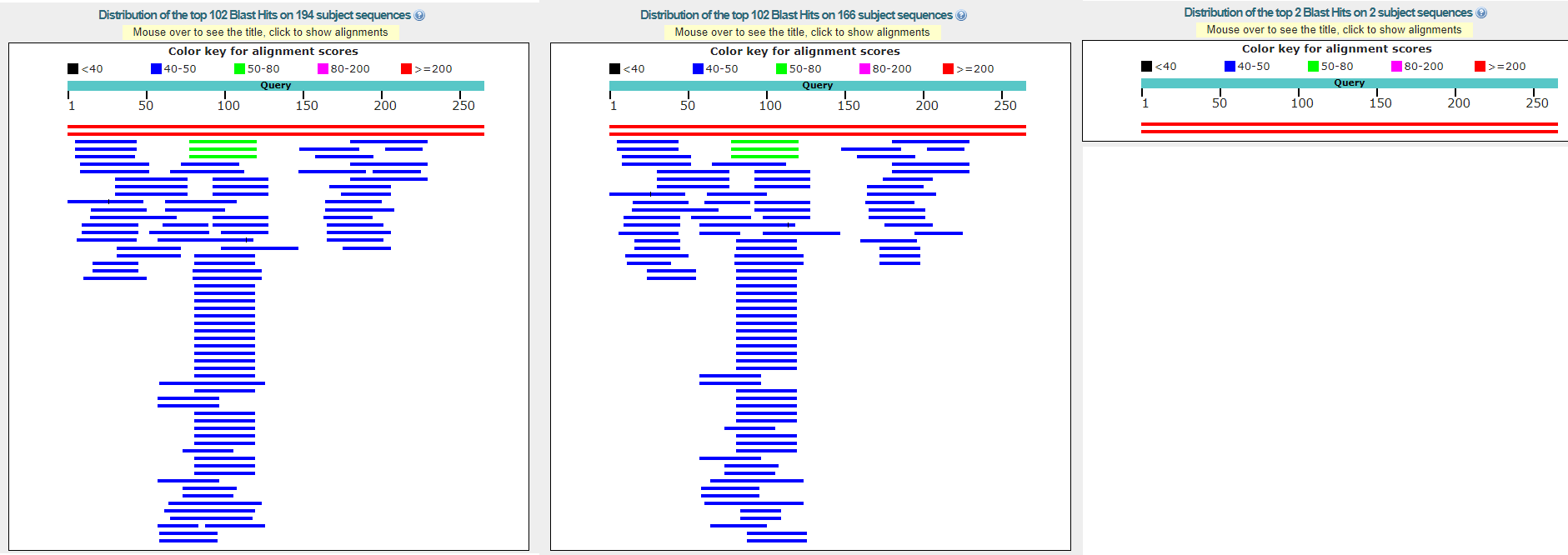
a more qualitative search with higher word size. One of the most interesting results is presented below: we can see, that in all runs with 1;-4 Match/Mismatch scores, lots of alignments contain 2 Matches,
while with default Match/Mismatch score it's only one Match.
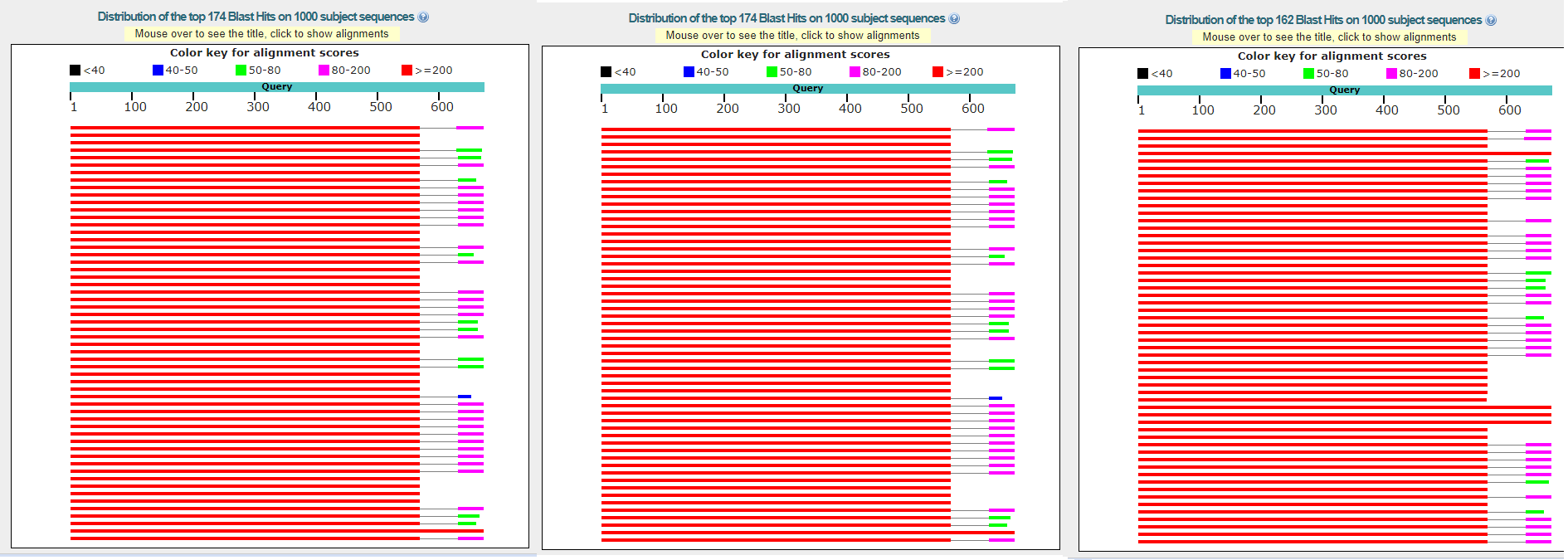
Alignment map for runs with 1;-4 Match/Mismatch scores
Alignment map for runs with defaults
It must be caused by less conservative part of rRNA gene between 2 Matches. So, it was decided to found, is the region between 2 matches in runs with 1;-4 Match/Mismatch conservative
or not.
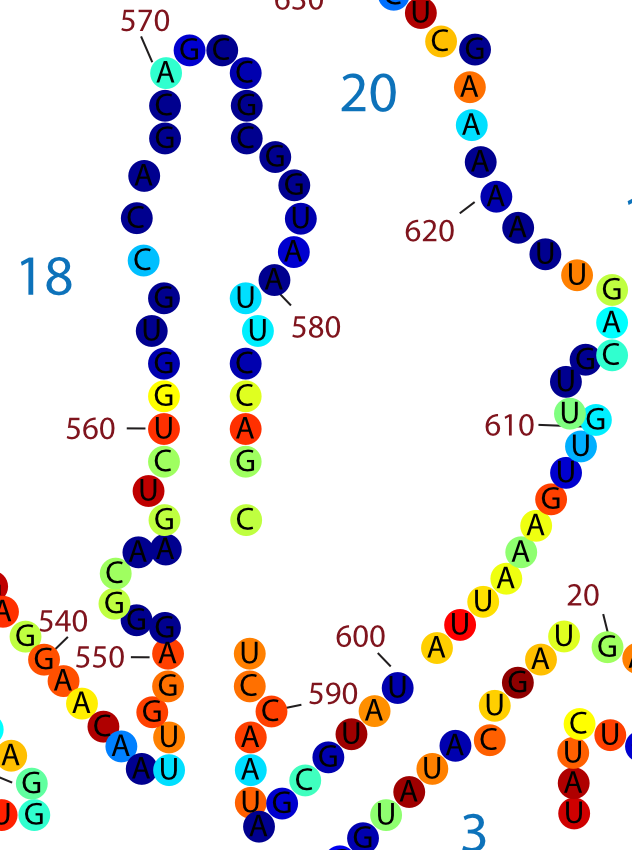
Here alignments for the same genes and the same algorithms, but with different Match/Mismatch scores is presented. Part, which is considered to be a non-conservative is marked with peppers.
To validate that hypothesis, the map of variable regions of rRNA was found. Here, nucleotides are coloured according to Shannon entropy index. Blue colour means that nucleotides are not conservative.
And we can see, that in the part, that we consider being a non-conservative (560-620), a majority of the nucleotides is coloured with blue or not-red colours, meaning that part is non-conservative really.
As a mitochodrion genome, it was decided to choose Microbotryum lychnidis-dioicae genome, and ncRNA with sequence:
taagggttgcaaagttgaaaacatactatttaaaattgtgtttttggaaagtcctaggtgtaagaaaatatacaaaatggatt
aaactatgacatacttacagaaatattatacttaaacttagactgtttacgtatcgaactgaagtctatatacactaccttat
tcagatttttaacaattaatcaacttaatatctcccctgccttttgatgaaaaaggaaagtggcttgatatacagaattaggc
ttatagcaaccctta
In result, there were much less alignments, than in previous runs. Blastn with word size 11 and defaults shows 166 findings, Blastn with 7-word size and defaults - 194 findings, and Megablast shows only
2 findings. All except 2 findings in all algorithms were senseless, they weren't even from mitochondrion genome. And that 2 findings were from mitochondrion genome of a different species of genus Microbotryum.
So, after the comparison of 3 different algorithms, we can conclude, that:
- Megablast algorithm is really works better with similar sequences, such as 18S rRNA gene sequences: it shows more similar alignments, while blastn algorithm is better for sequences with low level of
similarity.
- Changing of the selected taxonomical ranks could remarkable change the output.
- Changing the Match/Mismatch scores could expand horizons of bioinformatical research.
Homology rewiev
For that task, 3 proteins were chosen(PRPC_EMENI, TERT_SCHPO and TBB_NEUCR).
PRPC_EMENI
That mitochondrial enzyme exists in almost all eukaryotes, it participates in the Krebs cycle. It synthesizes by cytoplasmic ribosomes, and then transport
to the mitochondrion.
Score E
Sequences producing significant alignments: (Bits) Value
scaffold-693 393 1e-122
scaffold-157 390 1e-121
scaffold-287 64.3 8e-011
scaffold-212 57.4 1e-008
TBLASTN run shows 4 findings, 2 of them were with very low scores and bad e-values, so they should be an artefact of an algorithm, and other findings were
with quite good e-value, they contain long conservative regions, so we could say, that there is at least presumptive positive.
Score = 393 bits (1010), Expect = 1e-122, Method: Compositional matrix adjust.
Identities = 212/376 (56%), Positives = 269/376 (72%), Gaps = 6/376 (2%)
Frame = +1
Query 86 GIRFHGKTIKDCQKELPKGPTGTEMLPEAMFWLLLTGEVPSTSQVRAFSKQLAEE-SHLP 144
GIRF G TI +C ++LPK G E LPE +F+LLLTGEVP+ QV S+ A S LP
Sbjct 1243882 GIRFRGMTIPEC*EKLPKANGG*EPLPEGLFYLLLTGEVPTKEQVDEVSRDWANRASSLP 1244061
Query 145 DHILDLAKSFPKHMHPMTQISIITAALNTESKFAKLYEKGINKADYWEPTFDDAISLLAK 204
H+ D+ P +HPM+Q SI A+ +SKFA+ Y++G++K+ YWE ++D++ L+AK
Sbjct 1244062 KHVEDIID*CPVTLHPMSQFSIAVTAMQHDSKFAQAYQQGVHKSKYWEYAYEDSMDLIAK 1244241
Query 205 IPRVAALVFRPNEIDVVGRQKLDPAQDWSYNFAELLGKGGANNADFHDLLRLYLALHGDH 264
+P VA+ ++R N +D +DWSYNFA +LG G +A F +L+RLYL +H DH
Sbjct 1244242 LPVVASRIYR-NVFKDGKVAAIDKTKDWSYNFANMLGFG--KDAQFVELMRLYLTIHSDH 1244412
Query 265 EGGNVSAHATHLVGSALSDPFLSYSagllglagplhglaaQEVLRWILAMQEKIGTKFTD 324
EGGNVSAH THLVGSALSDP+LS++AGL GLAGPLHGLA QEVLRWIL M+E+IGT +D
Sbjct 1244413 EGGNVSAHTTHLVGSALSDPYLSFAAGLNGLAGPLHGLANQEVLRWILQMKEEIGTNVSD 1244592
Query 325 EDVRAYLWDTLKSGRVVPGYGHGVLRKPDPRFQALMDFAATRKDVLANPVFQLVKKNSEI 384
E VR Y W TLKSG+V+PGYGH VLRK DPR+ +FA K + +P+F++V + I
Sbjct 1244593 EQVRDYCWKTLKSGQVIPGYGHAVLRKTDPRYTCQREFAL--KHLPTDPLFKMVSQLYNI 1244766
Query 385 APGVLTEHGKTKNPHPNVDAASGVLFYHYGFQQPLYYTVTFGVSRALGPLVQLIWDRALG 444
P VLTE GKTKNP PNVDA SGVL HY ++ +YTV FGVSRALG L QL+WDRALG
Sbjct 1244767 VPNVLTEQGKTKNPFPNVDAHSGVLLQHYNLKEQEFYTVLFGVSRALGCLSQLVWDRALG 1244946
Query 445 LPIERPKSINLLGLKK 460
LPIERPKS+ +KK
Sbjct 1244947 LPIERPKSLTTDTIKK 1244994
First alignment(scaffold-693)
Score = 390 bits (1003), Expect = 1e-121, Method: Compositional matrix adjust.
Identities = 212/376 (56%), Positives = 268/376 (71%), Gaps = 6/376 (2%)
Frame = +2
Query 86 GIRFHGKTIKDCQKELPKGPTGTEMLPEAMFWLLLTGEVPSTSQVRAFSKQLAEE-SHLP 144
GIRF G TI +C ++LPK G E LPE +F+LLLTGEVP+ QV S+ A S LP
Sbjct 314582 GIRFRGMTIPEC*EKLPKANGG*EPLPEGLFYLLLTGEVPTKEQVDEVSRDWANRASSLP 314761
Query 145 DHILDLAKSFPKHMHPMTQISIITAALNTESKFAKLYEKGINKADYWEPTFDDAISLLAK 204
H+ D+ P +HPM+Q SI A+ +SKFA+ Y +G++K+ YWE ++D++ L+AK
Sbjct 314762 KHVEDIID*CPVTLHPMSQFSIAVTAMQHDSKFAQAY*QGVHKSKYWEYAYEDSMDLIAK 314941
Query 205 IPRVAALVFRPNEIDVVGRQKLDPAQDWSYNFAELLGKGGANNADFHDLLRLYLALHGDH 264
+P VA+ ++R N +D +DWSYNFA +LG G +A F +L+RLYL +H DH
Sbjct 314942 LPVVASRIYR-NVFKDGKVAAIDKTKDWSYNFANMLGFG--KDAQFVELMRLYLTIHSDH 315112
Query 265 EGGNVSAHATHLVGSALSDPFLSYSagllglagplhglaaQEVLRWILAMQEKIGTKFTD 324
EGGNVSAH THLVGSALSDP+LS++AGL GLAGPLHGLA QEVLRWIL M+E+IGT +D
Sbjct 315113 EGGNVSAHTTHLVGSALSDPYLSFAAGLNGLAGPLHGLANQEVLRWILQMKEEIGTNVSD 315292
Query 325 EDVRAYLWDTLKSGRVVPGYGHGVLRKPDPRFQALMDFAATRKDVLANPVFQLVKKNSEI 384
E VR Y W TLKSG+V+PGYGH VLRK DPR+ +FA K + +P+F++V + I
Sbjct 315293 EQVRDYCWKTLKSGQVIPGYGHAVLRKTDPRYTCQREFAL--KHLPTDPLFKMVSQLYNI 315466
Query 385 APGVLTEHGKTKNPHPNVDAASGVLFYHYGFQQPLYYTVTFGVSRALGPLVQLIWDRALG 444
P VLTE GKTKNP PNVDA SGVL HY ++ +YTV FGVSRALG L QL+WDRALG
Sbjct 315467 VPNVLTEQGKTKNPFPNVDAHSGVLLQHYNLKEQEFYTVLFGVSRALGCLSQLVWDRALG 315646
Query 445 LPIERPKSINLLGLKK 460
LPIERPKS+ +KK
Sbjct 315647 LPIERPKSLTTDTIKK 315694
Second alignment(scaffold-157)
TERT_SCHPO
Telomerase reverse transcriptase is a catalytic subunit of the telomerase, which is one of the most important unit of the telomerase complex. TERT is responsible for the addition of a TTAGGG sequence
to the end of a chromosome’s telomeres. This addition prevents degradation of the cells.
Score E
Sequences producing significant alignments: (Bits) Value
scaffold-17 108 1e-023
unplaced-307 102 7e-022
scaffold-105 33.9 0.51
unplaced-647 28.1 4.9
scaffold-170 30.0 7.6
TBLASTN run shows 5 findings and 3 of them were with very bad e-values and should be considered as an artefact,
and other findings were with bad e-values too, but not as bad, as previous, they contain short conservative parts and can't be interpreted unambiguously. That fact may be caused by different
Hayflick limits and lifespans in different organisms. Alignment with the best score is presented below
Score = 108 bits (269), Expect = 1e-023, Method: Compositional matrix adjust.
Identities = 123/491 (25%), Positives = 229/491 (47%), Gaps = 63/491 (13%)
Frame = +1
Query 320 HYCPYIDTHDDEKILSYSLKPNQVFAFLRSILVRVF-PKLIWGNQRIFEIILKDLETFLK 378
YCP + DD L+ +P+ V F+R +L++VF G + + + + L
Sbjct 610900 QYCPAQSSSDDGLTLNDYSRPHDVKQFVRCVLIKVFRCNFFGGMENLNAFVDNAVGMLLN 611079
Query 379 LSRYESF-SLHYLMSNIKISEIEWLVLGKRSNAKMCLSDFEKRKQ--IFAEFIYWLYNSF 435
L ++ES +++ I+ S I WL + K+ ++ E +K + + WL N F
Sbjct 611080 LRKFESMPEASFIVKGIQSSRIMWLRSKLNT*PKV-VNKLEHQKL**LCSSLFQWLLNRF 611256
Query 436 IIPILQSFFYITESSDLRNRTVYFRKDIWKLLCRPFITSMKMEAFEKINENNVRMDTQKT 495
+ +L++ F+IT++S +NR Y+R D+W+ R ++ I+ + +T +
Sbjct 611257 VSDLLKACFFITDTSHCKNRVFYYRFDLWR---RMVEVQSSIKNLHPIDMG*I--NTGRK 611421
Query 496 TLPPAVIRLLPKKN-TFRLITNLRKRFLIKMGSNKKM--LVSTNQTLRPVASILKHLINE 552
+ + IRL+PK+N +FR I NLR + +NK M L+S + L++E
Sbjct 611422 FM--S*IRLIPKENGSFRRINNLR-----SVNNNK*MYGLLSDA*CI---------LLSE 611553
Query 553 ESSG--------IPFNLEVYMKLLTFKKDLLKHRMFGRKKYFVRIDIKSCYDRIKQDLMF 604
++ G + N ++Y +L FK G YFV+ D+ YD I + +F
Sbjct 611554 KNYG*IDLLKDIVLSNDDIYARLK*FKMRNKARF*RGD*LYFVKSDVT*AYDSINRQKLF 611733
Query 605 RIVKKKL-KDPEFVIRKYATI-------------HATSDRATKNFVSEAFSYFDMVPFEK 650
+++ D EF+I Y H S RA + F +
Sbjct 611734 SVLE*IF**DSEFIIHGY*R*LQLCLLR*F*KLYHKVSIRAE*H-----------QTFPE 611880
Query 651 VVQLLSMKTSDTLFVDFVDYWTKSSSEIFKMLKEHLSGHIVKIGNSQYLQKVGIPQG-SI 709
+ L+ ++ +F+D V S +++FK +++ + +I++ + Y+Q+ GIPQG +
Sbjct 611881 FCKELAKSIANKVFIDKV**KKVSGADVFKAIEQLIYDNILQFEDGYYVQEEGIPQGSIV 612060
Query 710 LSSFLCHFYMEDLIDEYLSFTKKKGSVLLRVVDDFLFITVNKKDAKKFLNLSLRGFEKHN 769
S Y ++E +FT++ S+L++ +DDFL++T +K A +L+ GF +
Sbjct 612061 SSLLCSLLYSHLALNELFTFTRRSDSLLIKFIDDFLYLTFDKA*A*GYLSRI*IGFPDYG 612240
Query 770 FSTSLEKTVIN 780
+ +KT N
Sbjct 612241 VHMNPKKTATN 612273
TBB_NEUCR
Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It's critical for healthy functioning in almost all cells. So it's unsurprisingly, that in the output of TBLASTN 5 alignments with relatively good e-values are
presented. Best alignment is shown below.
Score E
Sequences producing significant alignments: (Bits) Value
unplaced-665 742 0.0
scaffold-26 693 0.0
scaffold-57 348 3e-107
unplaced-5 348 4e-107
scaffold-423 161 6e-049
Score = 742 bits (1915), Expect = 0.0, Method: Compositional matrix adjust.
Identities = 367/450 (82%), Positives = 398/450 (88%), Gaps = 22/450 (5%)
Frame = -2
Query 1 MREIVHLQTGQCGNQIGAAFWQTISGEHGLDASGVYNGTSELQLERMN------------ 48
MREIVHL TG CGN IGA FW+ IS EHG+D +G Y G S+LQLER+N
Sbjct 7236 MREIVHL*TG*CGN*IGAKFWEVISDEHGIDPNGRYEGDSDLQLERINGEFLNVLFCA** 7057
Query 49 ----------VYFNEASGNKYVPRAVLVDLEPGTMDAVRAGPFGQLFRPDNFVFGQSGAG 98
VYFNEASG KYVPRAVLVDLEPGTMD+VRAGP+G LFRPDNF+FGQSGAG
Sbjct 7056 AFCITLLLIVVYFNEASGGKYVPRAVLVDLEPGTMDSVRAGPYGNLFRPDNFIFGQSGAG 6877
Query 99 NNWAKGHYTEGAELVDQVLDVVRREAEGCDCLQGFQITHSlgggtgagmgtllISKIREE 158
NNWAKGHYTEGAELVD VLDVVR+EAEGCDCLQGFQITHSLGGGTGAGMGTLLISKIREE
Sbjct 6876 NNWAKGHYTEGAELVDSVLDVVRKEAEGCDCLQGFQITHSLGGGTGAGMGTLLISKIREE 6697
Query 159 FPDRMMATFSVVPSPKVSDTVVEPYNATLSVHQLVENSDETFCIDNEALYDICMRTLKLS 218
+PDRMM TFSVVPSPKVSDTVVEPYNATLSVHQLVENSDETFCIDNEALYDIC RTLKL+
Sbjct 6696 YPDRMMCTFSVVPSPKVSDTVVEPYNATLSVHQLVENSDETFCIDNEALYDICFRTLKLT 6517
Query 219 NPSYGDLNHLVSAVMSGVTVSLRFPGQLNSDLRKLAVNMVPFPRLHFFMVGFAPLTSRGA 278
P+YGDLNHLVSAVMSGVT S+RFPGQLN+DLRKLAVNMVPFPRLHFFMVGFAPLTSRG+
Sbjct 6516 TPTYGDLNHLVSAVMSGVTTSIRFPGQLNADLRKLAVNMVPFPRLHFFMVGFAPLTSRGS 6337
Query 279 HHFRAVSVPELTQQMFDPKNMMAASDFRNGRYLTCSAIFRGKVSMKEVEDQMRNVQNKNS 338
+RA+SV ELT QMFD KNMMAASD R+GRYL +AIFRGK+SMKEV++QM +VQ KNS
Sbjct 6336 QQYRALSVAELTTQMFDAKNMMAASDPRHGRYLAVAAIFRGKMSMKEVDEQMLSVQTKNS 6157
Query 339 SYFVEWIPNNVQTALCSIPPRGLKMSSTFVGNSTAIQELFKRIGEQFTAMFRRKAFLHWY 398
SYFVEWIPNNV+TA+C IPP+GLKMS+TF+GNSTAIQELFKRI +QF+ MF+RKAFLHWY
Sbjct 6156 SYFVEWIPNNVKTAVCDIPPKGLKMSATFIGNSTAIQELFKRISDQFSVMFKRKAFLHWY 5977
Query 399 TGEGMDEMEFTEAESNMNDLVSEYQQYQDA 428
TGEGMDEMEFTEAESNMNDLVSEYQQYQDA
Sbjct 5976 TGEGMDEMEFTEAESNMNDLVSEYQQYQDA 5887
Best alignment
Searching gene in contigs
For the current task blastx algorithm was used. In contig "unplaced-921", there was one finding, corresponding to be a MCM-domain-containing protein with strong e-value.
That protein is essential for genomic DNA replication. MCM is a target of different replication checkpoint pathways, such as the S-phase entry.
Deregulation of MCM function has been linked to genomic instability and a variety of carcinomas (in humans)
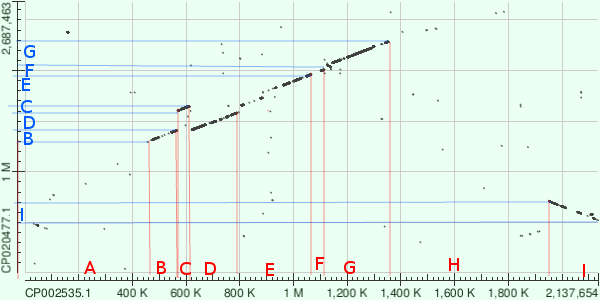
Dot matrix map
Dot matrix map, parts of a genome is marked with letters
© Gumerov Ruslan, 2017