Picture 1.The representation of pairwise global alignment.
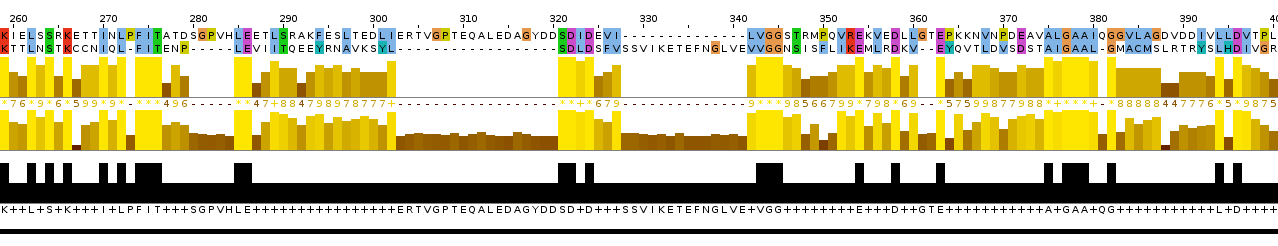
According the task of pr 11 I used two homologous protein sequences from pr 10 and campared their pairwise global and local alignments. I used "needle" (EMBOSS) for global alignment and "water" (EMBOSS) for local alignment. Then I used "infoalign" (EMBOSS) to find out the characteristics of these alignments (see tables 1, 2). To represent the results I used Jalview (program Tcoffee with Defaults, colored by ClustalX, with Identity Threshold = 100%).
Table 1.The parametres of grobal alignment.
| Name | SeqLen | AlignLen | GapLen | % of GapLen | Absolutely Ident | % of Abs. Ident | Functional Ident | % of Func. Ident |
| DNAK_HALWD | 641 | 692 | 51 | 7,37 | 140 | 20,23 | 270 | 39,02 |
| HSP7F_ENCCU | 658 | 769 | 111 | 14,43 | 140 | 18,21 | 270 | 39,02 |
! To see the whole picture press on it.
Picture 1.The representation of pairwise global alignment.

Table 2.The parametres of local alignment.
| Name | SeqLen | AlignLen | GapLen | % of GapLen | Absolutely Ident | % of Abs. Ident | Functional Ident | % of Func. Ident |
| DNAK_HALWD | 581 | 618 | 37 | 5,99 | 135 | 21,84 | 254 | 41,10 |
| HSP7F_ENCCU | 534 | 618 | 84 | 13,59 | 135 | 21,84 | 254 | 41,10 |
! To see the whole picture press on it.
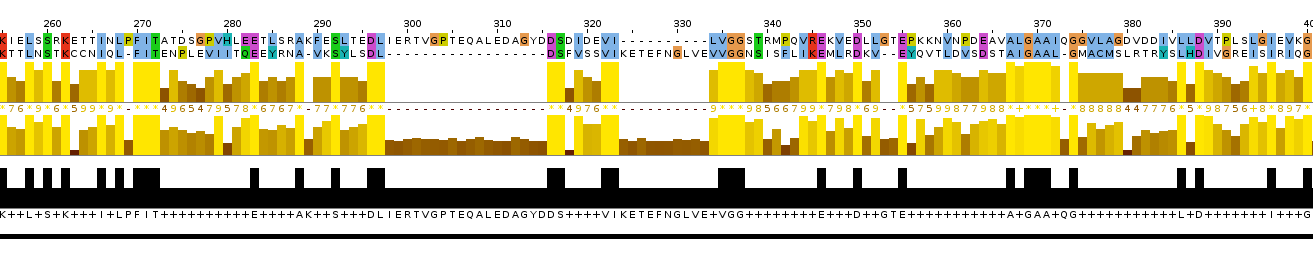
Picture 2.The representation of pairwise local alignment.
By command "needle -help -verbose" and "water -help -verbose" I found out a system of penalties which is used to make alignments (see table 3). This information is included in units "Stundart qualifiers" and "Additional qualifiers".
Table 3.Penalties for gaps in different cases.
| Program | The gap open penalty inside the sequense | The gap extension penalty is added to the standard gap penalty for each residue in the gap | The terminal gap open penalty | The gap extension penalty is added to the standard terminal gap penalty for each residue in the gap |
| Needle | 10.0 [1.0 - 100.0] | 0.5 [0.0 - 10.0] | 10.0 [1.0 - 100.0] | 0.5 [0.0 - 10.0] |
| Water | 10.0 [1.0 - 100.0] | 0.5 [0.0 - 10.0] | NO | NO |
According the task I compared pairwise local alignments of two homologous and five pairs of nonhomologous proteins. The homologous protein sequences were taken from task 1. As nonhomologous protein sequences I used "my protein" (pr 1) and five proteins randomly chosen between "my classmate's proteins". You can see some infirmation about these proteins in table 4. Line with "my protein" is in bold.
Table 4. Some information about proteins which I used.
| Entry name | SeqLen | Protein name | Organism |
| DNAK_HALWD | 641 | Chaperone protein DnaK | Haloquadratum walsbyi |
| HSP7F_ENCCU | 658 | Heat shock protein homolog SSE1 | Encephalitozoon cuniculi |
| A0A0U3W9X5_9BACI | 322 | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase | Lentibacillus amyloliquefaciens |
| A0A0U3QLP1_9MICC | 242 | ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase | Arthrobacter sp. |
| A0A0X8CMX2_9BRAD | 772 | Uncharacterized protein | Bradyrhizobium sp. |
| A0A0U3QKR4_9MICC | 444 | Alpha-L-fucosidase | Arthrobacter sp. |
| A0A0F6CLF2_MYCGL | 1269 | CRISPR-associated endonuclease | Mycoplasma gallisepticum |
| A0A0H4VDW6_9SPHN | 768 | Cell division cycle protein | Erythrobacter atlanticus |
Table 5.The parametres of local alignment of two homologous proteins and five pairs of nonhomologous proteins.
| Name | SeqLen | AlignLen | % of SeqLen in local alignment in compare with protein length | GapLen | % of GapLen | Absolutely Ident | % of Abs. Ident | Functional Ident | % of Func. Ident |
| DNAK_HALWD | 581 | 618 | 90,64 (581/641) | 37 | 5,99 | 135 | 21,84 | 254 | 41,10 |
| HSP7F_ENCCU | 534 | 618 | 81,16(534/658) | 84 | 13,59 | 135 | 21,84 | 254 | 41,10 |
| A0A0U3W9X5_9BACI | 74 | 76 | 22,98 (74/322) | 2 | 2,63 | 21 | 27,63 | 31 | 40,79 |
| A0A0U3QLP1_9MICC | 73 | 76 | 30,17 (73/242) | 3 | 3,95 | 21 | 27,63 | 31 | 40,79 |
| A0A0U3W9X5_9BACI | 176 | 223 | 54,66 (176/322) | 47 | 21,08 | 44 | 19,73 | 75 | 33,63 |
| A0A0X8CMX2_9BRAD | 198 | 223 | 25,65 (198/772) | 25 | 11,21 | 44 | 19,73 | 75 | 33,63 |
| A0A0U3W9X5_9BACI | 174 | 211 | 54,04 (174/322) | 37 | 17,54 | 41 | 19,43 | 65 | 30,81 |
| A0A0U3QKR4_9MICC | 153 | 211 | 34,46 (153/444) | 58 | 27,49 | 41 | 19,43 | 65 | 30,81 |
| A0A0U3W9X5_9BACI | 34 | 57 | 10,56 (34/322) | 23 | 40,35 | 14 | 24,56 | 20 | 35,09 |
| A0A0F6CLF2_MYCGL | 57 | 57 | 4,49 (57/1269) | 0 | 0 | 14 | 24,56 | 20 | 35,09 |
| A0A0U3W9X5_9BACI | 212 | 320 | 65,84 (212/322) | 108 | 33,75 | 67 | 20,94 | 105 | 32,81 |
| A0A0H4VDW6_9SPHN | 315 | 320 | 41,02 (315/768) | 5 | 1,56 | 67 | 20,94 | 105 | 32,81 |
Picture 3.The representation of pairwise local alignment of two nonhomologous protein sequences.
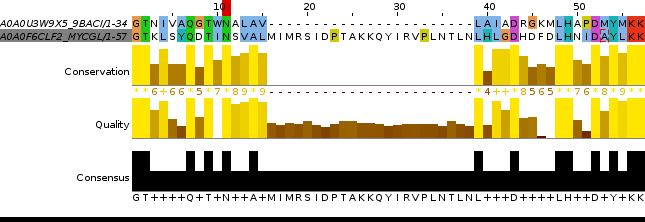
! To see the whole picture press on it.
Picture 4.The representation of alignment: the cut out piece of multiple alignments and the global alignment.
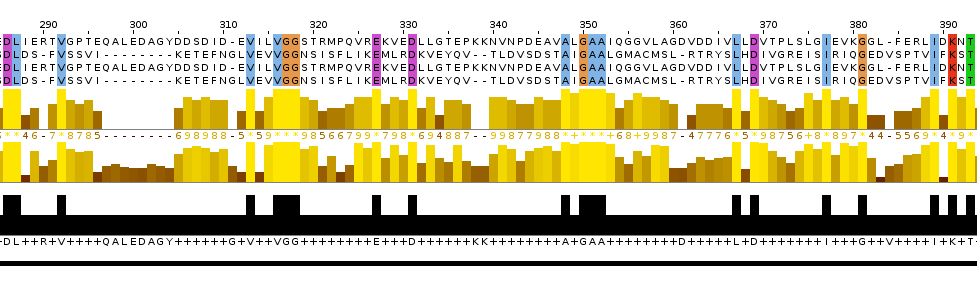
Picture 5.The representation of alignment: the cut out piece of multiple alignments and the local alignment.
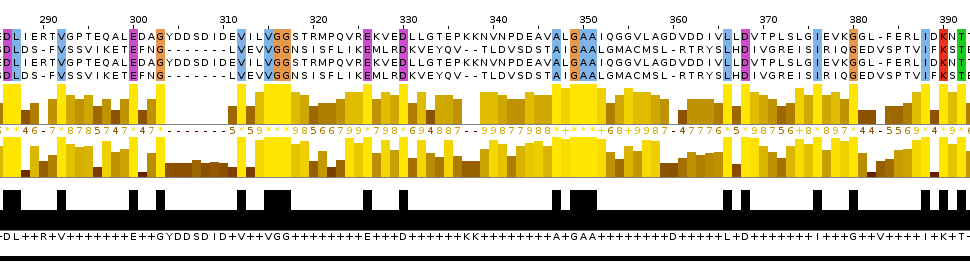
Picture 6.The representation of alignment: the global alignmetn and the local alignment.
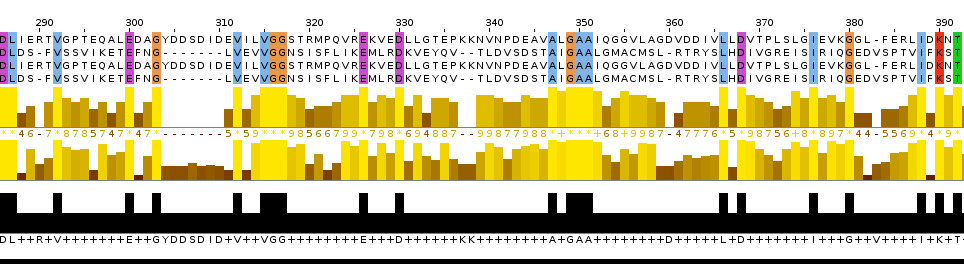
The conclusion:
I think that the local alignment is more reliable than global and the cut out piece of multiple alignment. Reasons: 1. the site which was discussed above contains more conserved columns in local alignment than in global; 2. this site contains two starts of gaps in the global alignment and only one in the local one.