| FBB MSU site | Main page | About me | Terms |
Sanger sequencing
Supplementary downloads
- Original sequences: forward and reverse.
- Corrected sequenses: forward and reverse.
- Alignment of corrected sequences: Jalview progect (fasta format).
Task 1
According the task I download two files contained forward and reverse sequences of DNA sequenced by Sanger method (see "Supplementary downloads"). I compared the forward sequence and reverse one transformed by "Reverse+Complement" to make corrections. Sequences were visualised by Chromas lite 2.6.5 version.
Quality evaluation of chromatograms:
- Lenghth of the forward sequence is 930 bases, interval with good readability is 724 bases. Lenghth of the reverse sequence is 951, interval with good readability is 705 bases. The boundaries of the ends of the readable interval you can see in the table 1. There are also similar data defined automatically with the default settings and enabled "Trim Low Quality" (TLQ). (Seq. was cut like show in the columns "real").
Table 1.
Sequense 5' (real) 3' (real) 5' (automat.) 3' (automat.) 5' (automat. TLQ) 3' (automat. TLQ) forward 30 754 51 719 31 877 reverse
(after Reverse+Complement)201 926 212 899 124 923 - The unreadable part to whole lenght ratio 22% for forward seq. and 25% for reverse one. This means that at the ends of the sequence a fairly large semantic fragments is lost.
- The level of noise through readable interval is about 10-20%. I think the signal-to-noise ratio allows us to consider the read reliable.
- There are peaks with high intensity and increased noise level through unreadable intervals.
Correcting of the cromatograms. Problematic nucleotides.
As I said I compared the forward sequence and reverse one transformed by Reverse+Complement function to make corrections in forward one. I suspected that positions 269 and 443 are polymorphisms. But there wasn't signs of polymorphism through the reverse sequence, so I deside that I can reconstruct these problematic nucleotides exactly as they are in reverse seq. (see pic. 1-2)
Picture 1-2.
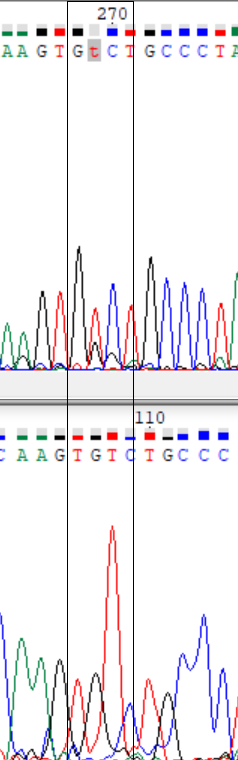
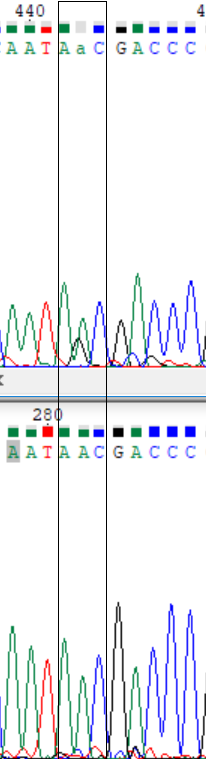
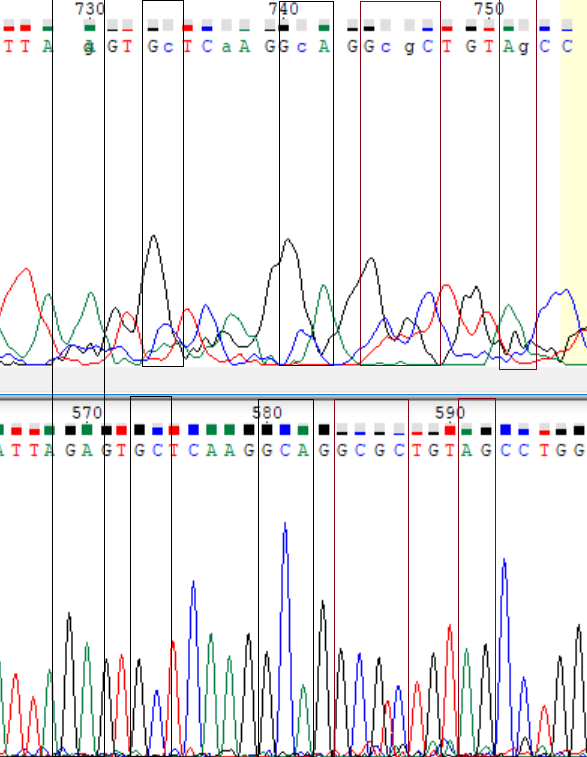
Here are examples of the too weak signal (597) and signals are overlaping with other ones (641, 647, 648). These nucleotides were restored with the reverse chain.
Picture 3.
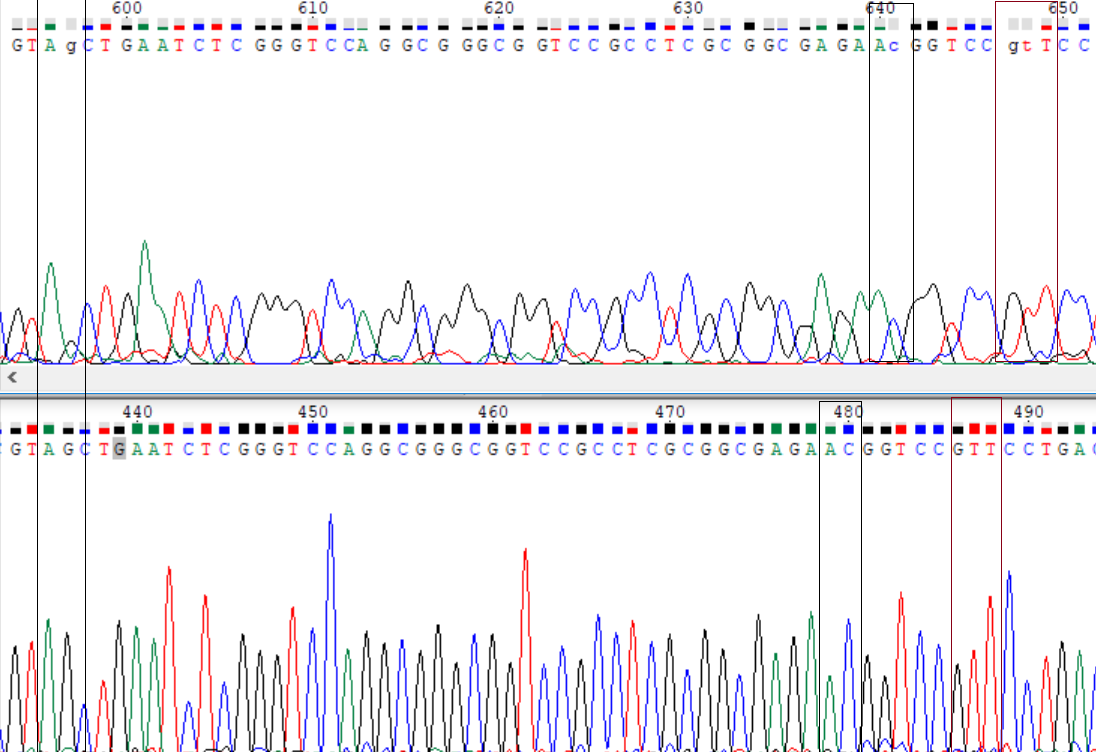
Here is the region I did was able to reconstruct with reverse seq., but it isn't very reliable reconstruction because signals are overlaping too much and they have different intensity.
Picture 4.
Alignment.
Using needle (syntax "needle -aformat fasta filename1 filename2") I aligned corrected forward and reverse sequences. You can download the alignment in fasta format in "Supplementary downloads" and see pic. 5.
Picture 5. The representation of alignment.

Task 2
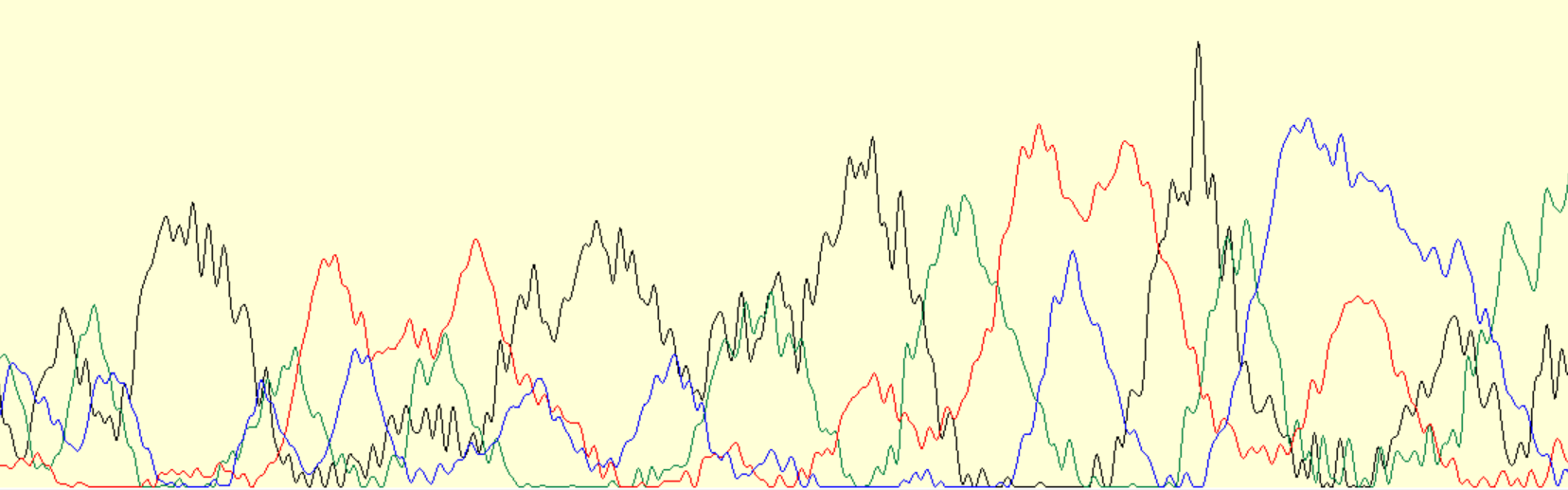
There is an example of unreadable intervals of the chromatogram from the end of the sequence (see pic. 6). It is unreadable because of following factors. Firstly, signals have very different intensities so we can't distinguish real signals from noise. Secondly, peaks are overlaping too mach to divide them. And finally the peaks are strongly stretched horizontally so we aren't able to determine the number of nucleotides.
Picture 6.
| Term 3 |
| ← Block 1 | Pr 7 → |
© Darya Potanina, 2017