BLAST and similarity search
Last updated: 9-05-2017.
Files to download
Task 1. Homology of proteins found by similarity
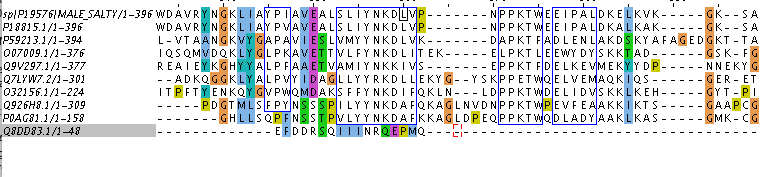
To search for homology, 9 proteins were taken from BLAST output (Swiss-Prot database was used, word size was changed from 6 to 3). As a result of their comparison, Table 1 was created. Figure 1 contains alignment of them with 'blocks' bordered. According to Figure 1, first 8 of 9 sequences are seeming like homologous, but I am still not sure about eighth one (P0AG81.1). Assuming Q926H8.1 and P0AG81.1 are homologous, so P0AG81.1 should be homologous to the rest of observed proteins (according to the criterion of transition forms) Conclusions about homology were based on data about E-value and identity from Table 1 and on information about blocks from Figure 1. Notes for Figure 1'2: even selected block has gaps, they are the same for both sequences, so it is possible not to take them into account.
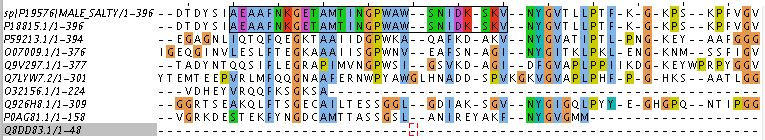
| Uniprot AC | Protein name | Coverage, % | Identity, % | E-value | Homology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P19576 | Maltose-binding periplasmic protein | 100 | 100 | 0 | N/A |
| P18815.1 | Maltose-binding periplasmic protein | 100 | 93 | 0 | + |
| P59213.1 | Maltose/maltodexrin-binding periplasmic protein | 97 | 31 | 6e-37 | + |
| O07009.1 | Cyclodextrin-binding protein | 91 | 31 | 2e-35 | + |
| Q9V297.1 | Maltotriose-binding protein | 93 | 28 | 6e-31 | + |
| Q7LYW7.2 | Trehalose/maltose-binding protein | 69 | 28 | 2e-13 | + |
| O32156.1 | Uncharacterized ABC transporter extracellular-binding protein | 53 | 26 | 7e-06 | + |
| Q926H8.1 | sn-glycerol-3-phosphate-binding periplasmic protein | 69 | 24 | 8e-06 | + |
| P0AG81.1 | sn-glycerol-3-phosphate-binding periplasmic protein | 37 | 27 | 0.004 | + |
| Q8DD83.1 | Protein CyaY | 12 | 31 | 8.8 | - |
Table 1. Properties of several sequences from BLAST output.
Task 2. Major rearrangements between a pair of proteins having homologous domains
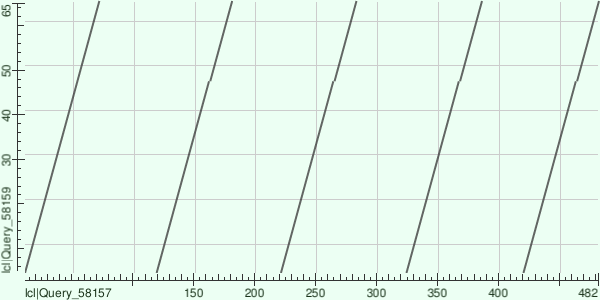
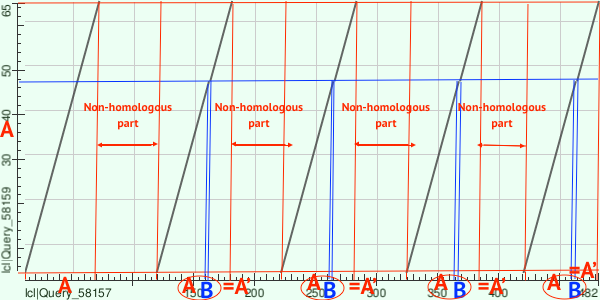
Family of LIM proteins from Pfam was chosen for this task due to its specific site architecture. Proteins with AC Q24400 and W5N561 were chosen. Their domain structure is shown in Figure 2. Figure 3 contains dot matrix of observed proteins. According to mapping from Figure 4, there are several evolution events could happen: first 'A' plot from W5N561 could be duplicated with insertion mapped as 'B'. Then this plot (A+B mapped as A') could duplicate 4 more times.