Uniprot acquaintance
Information about Maltose-binding periplasmic protein
Last updated: 14-03-2017.
Main Information about protein
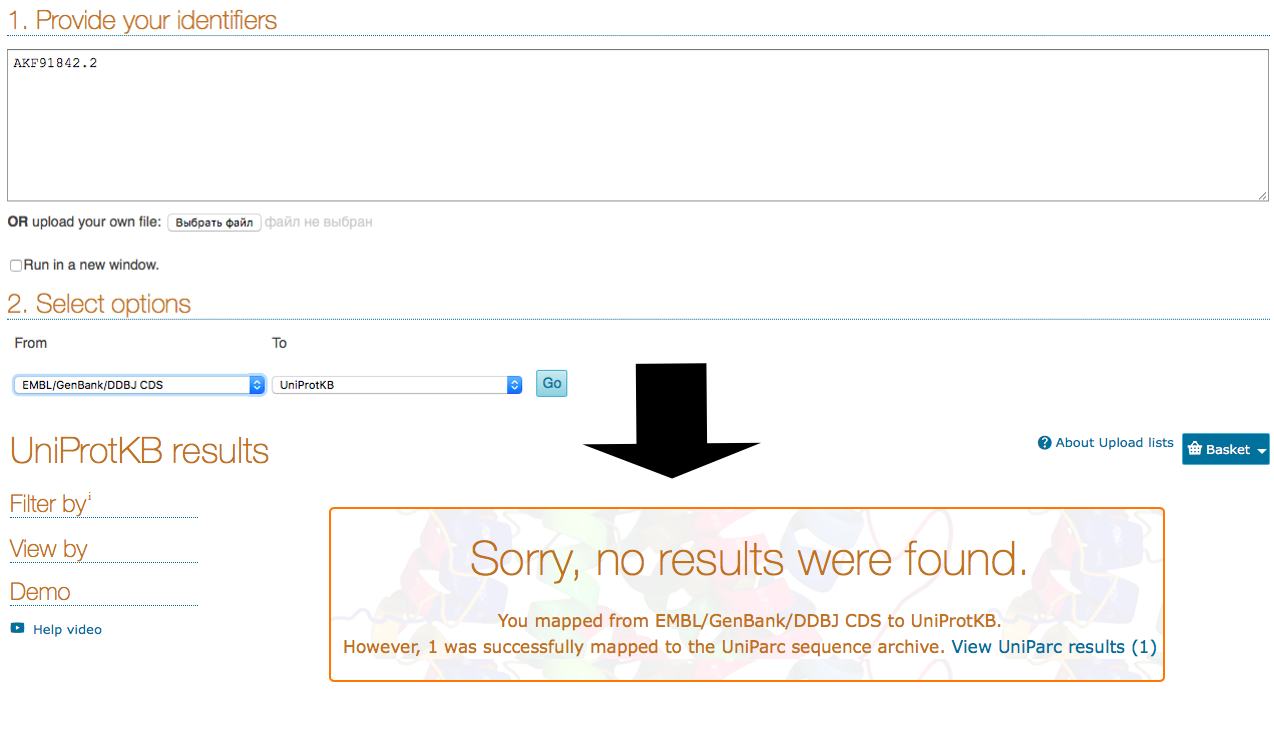
Unfortunately, it was not possible to find protein's Uniprot record using GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ banks (Fig. 1), so its PDB ID (3JYR) was used. It is important to note that detected record (P19576) doesn't belong to Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Anatum str. USDA-ARS-USMARC-1735, but it belongs to related species Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720). According to "DE" field in record, protein recommended name is Maltose-binding periplasmic protein. Information about protein IDs in different databases is contained in Table 1. Some facts about protein are located in Table 2. Maltose-binding periplasmic protein (MBP) is involved in maltose membrane transport system. It works like initial receptor for the active transport of maltooligosaccharides. Also it is a part of chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides. According to (DR, PDB) field, PDB site itself and KW field, protein is fully sequenced and its structure received using X-ray methods with the resolution of 1.75 A. MBP consists of the only one chain. Protein sequence is provided in Insertion. 1.
| Database | ID |
|---|---|
| Uniprot (AC) | P19576 |
| Uniprot (ID) | MALE_SALTY |
| PDB | 3JYR |
| RefSeq Protein | WP_000695417.1 |
Table 1. Protein IDs in different databases[0].
| Field in Uniprot record | Refinement | Value |
|---|---|---|
| DE, AltName | Alternative protein names | MBP, MMBP, Maltodextrin-binding protein |
| DE, RecName | Recommended protein name | Maltose-binding periplasmic protein |
| PE | Protein evidence | 1: Evidence at protein level |
| FT, SIGNAL | Signal sequence aminoacids | 1...26 |
| FT, CHAIN | Chains coordinates | 27...396 |
| FT | Amount of helices | 18 |
| FT | Amount of strands | 15 |
| SQ | Length | 396 AA |
| SQ | Molecular weight | 43181 |
Table 2. Some information about Maltose-binding periplasmic protein from Uniprot record[0].
MKIKTGVGIL ALSALTTMMI SAPALAKIEE GKLVIWINGD KGYNGLAEVG KKFEQDTGIK
VTVEHPDKLE EKFPQVAATG DGPDIIFWAH DRFGGYAQSG LLAEVTPDKA FQDKLYPFTW
DAVRYNGKLI AYPIAVEALS LIYNKDLVPN PPKTWEEIPA LDKELKVKGK SAIMFNLQEP
YFTWPLIAAD GGYAFKFENG KYDVKDVGVD NAGAKAGLTF LIDMIKNKNM SADTDYSIAE
AAFNKGETAM TINGPWAWSN IDKSKVNYGV TLLPTFKGKP SKPFVGVLSA GINAASPNKE
LAKEFLENYL LTDQGLEAVN KDKPLGAVAL KSFQEQLAKD PRIAATMDNA QKGEIMPNIP
QMSAFWYAVR TAVINAASGR QTVDAALKDA QSRITKInsertion 1. MBP sequence.
UniRef clusters
UniRef100: cluster ID is UniRef100_P19576, it contains 9 proteins. Only one of them is reviewed (Swiss-Prot). All nine proteins belong to Salmonella enterica. This fact does not contradict to systematics data and even proves them. Seed protein ID is A0A0F6BA72 and it is 475 AA long.
UniRef90: cluster ID is UniRef90_P19576, it contains 16 proteins. There is only one reviewed protein, too. And again, all proteins belong to Salmonella enterica. It shows that structure of such important protein as MBP shouldn't change widely. Seed protein ID is Q57GZ8 and it is 475 AA long.
UniRef50: cluster ID is UniRef50_P19576, it contains 608 proteins. 4 of them are reviewed. This cluster contains proteins from a large number of bacteria from different systematic groups. This fact emphasises the importance of fundamental role MBP playing in bacterial cell. Maltooligosaccharides are important nutritive substrate so species that are able to digest them receive an advantage over ones who's unable. Seed protein ID is D2TSM5 and it is 478 AA long.
Uniprot search queries
Basic information about search queries is presented in Table 3.
Query 'name:"maltose binding periplasmic protein" ' (Table 3, line 1): proteins from such popular organisms were found: Escherichia coli (strain K12), Enterobacter aerogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Photorhabdus luminescens, Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720). 432 of all proteins were found in bacteria, 8 in Archaea and information about 3 proteins was obtained from metagenetic data (Fig. 2).

Query 'lysozyme' (Table 3, line 4): lysozyme is a protein damaging bacterial cell walls by catalysing the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. It presented in all major groups of animals (Fig. 3)[1].

Query 'name:inhibitor name:trypsin' and 'name:trypsin' (Table 3, line 7&8): it is remarkable that trypsin inhibitors are better annotated than trypsin (7.06% against 2.34%). I suggest it could be connected with higher practical use potential of trypsin inhibitors.
| Search query | Total amount of proteins | Reviewed proteins | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| name:"maltose binding periplasmic protein" | 435 | 6 | Query by recommended name |
| name:"maltose binding periplasmic protein" organism:"salmonella typhimurium strain lt2 sgsc1412 atcc 700720" | 1 | 1 | Query by recommended name and organism |
| name:"maltose binding periplasmic protein" taxonomy:"Enterobacteriaceae [543]" | 167 | 5 | Query by recommended name and organism family |
| name:lysozyme | 17921 | 229 | Lysozyme in all groups of animals |
| name:lysozyme taxonomy:arthropoda | 583 | 17 | Lysozyme in Arthropoda |
| name:lysozyme taxonomy:viridiplantae | 17 | 3 | Lysozyme in Viridiplantae |
| name:trypsin | 13241 | 310 | Trypsin in all groups of animals |
| name:inhibitor name:trypsin | 2962 | 209 | Trypsin inhibitors in all groups of animals |
Table 3. Uniprot queries.
MBP in RefSeq Protein databases
According to Table 1, MBP has WP_000695417.1 identifier in RefSeq Protein database. This record is more laconic than Uniprot one, but contains less information overall. For example, there is no information about helices, strands and turns. Also there is no info about available publications connected with the protein in question, no other databases references. One more contrast: Uniprot record has information about protein from specific organism whereas RefSeq record represents a single, non-redundant, protein sequence which may be annotated on many different RefSeq genomes from the same, or different, species.[2]
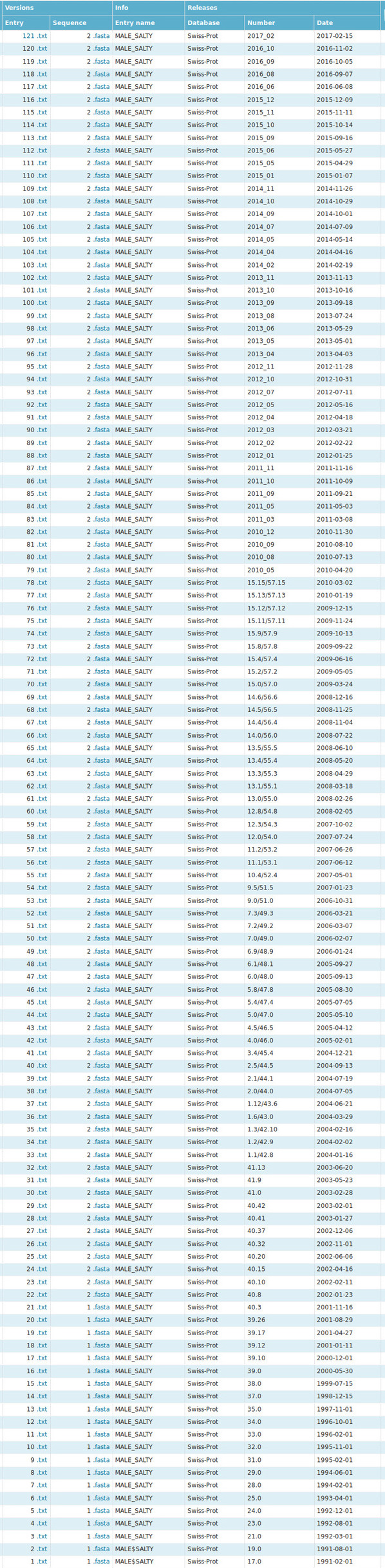
History of MBP changes
The whole history of MBP changes is presented in Fig. 4. As we can observe, the first record was made on 1991-02-01 and it is regularly updated (121 times) until now (last change was made on 2017-02-15). Based on this, it can be concluded that MBP is well studied protein.
Representation of modified residues in Uniprot
Information about representation of modified residues in Uniprot is assembled in Table 4. During the creation of the table, Uniprot help was used [3].
| Modification | Example from Uniprot record |
|---|---|
| Phosphorylation | FT MOD_RES 27 27 Phosphothreonine; by PLK1.
FT {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18174154,
FT ECO:0000269|PubMed:18418051}. |
| Carboxyl methylation | FT MOD_RES 309 309 Leucine methyl ester.
FT {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8206937}. |
| Nitrogen methylation | FT MOD_RES 2 2 N-methylalanine.
FT {ECO:0000269|PubMed:786732}. |
| Histidine methylation | FT MOD_RES 107 107 Pros-methylhistidine.
FT {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P50116}. |
| Lysine methylation | FT MOD_RES 36 36 N6-methyllysine.
FT {ECO:0000269|PubMed:3467365}. |
| Arginine methylation | FT MOD_RES 320 320 Dimethylated arginine; in A2780 ovarian
FT carcinoma cell line. {ECO:0000269|Ref.7}. |
| Acetylation | FT MOD_RES 2 2 N-acetylserine.
FT {ECO:0000244|PubMed:22814378, |
| Terminal amidation | FT MOD_RES 4 4 Phenylalanine amide. |
| Glutamate amidation | FT MOD_RES 349 349 Glutamic acid 1-amide.
FT {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8101868}. |
| Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid | FT MOD_RES 36 36 Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid. |
| Isomerization | FT MOD_RES 2 2 D-phenylalanine.
FT {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2597281}. |
| Hydroxylation | FT MOD_RES 39 39 4-hydroxyproline.
FT {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02745}. |
| Sulfation | FT MOD_RES 11 11 Sulfotyrosine.
FT {ECO:0000269|PubMed:5970899}. |
Table 4. Residues modifications.
References
[0] Maltose-binding periplasmic protein Uniprot record.
[1] Lysozyme, Wikipedia.
[2] MBP (WP_000695417.1), RefSeq Protein.
[3] Uniprot help, modified residue.