Resequencing. Search for polymorphisms in humans
Last updated: 27-11-2017.
Command table
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| fastqc chr8.fastq | FastQC reads a set of sequence files and produces from each one a quality control report consisting of a number of different modules, each one of which will help to identify a different potential type of problem in your data. |
| java -jar /usr/share/java/trimmomatic.jar SE -phred33 chr8.fastq chr8_trimmomatic.fastq TRAILING:20 MINLEN:50 | This command cuts off parts with average quality less than 20 and removes reads that are less than 50 nucleotides long. Quality changes are presented in Fig.1 and 2 |
| hisat2-build chr8.fasta processed | Indexing of reference sequence |
| hisat2 -x processed -q chr8_trimmomatic.fastq -S chr8.sam --no-spliced-alignment --no-softclip --met-file hisat2.txt | Alignment of reads and reference sequence |
| samtools view -b chr8.sam -o chr8.bam | Conversion of alignment into binary format |
| samtools sort chr8.bam sorted_8.bam | Alignment sorting by the coordinate in the reference |
| samtools index sorted_8.bam | Indexing of sorted file |
| samtools mpileup -I sorted_8.bam -uf chr8.fasta -g -o poly.bcf | Generating of file containing polymorphisms |
| bcftools call -cv poly.bcf -Ov -o snp.vcf | Generating of file containing list of differences between reference and reads |
| perl /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/convert2annovar.pl -format vcf4 snp.vcf > snp.avinput | Change file format to suitable for annovar |
| perl /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/annotate_variation.pl -out refgene -build hg19 snp.avinput /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/humandb/ | Annotate SNPs in refgene |
| perl /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/annotate_variation.pl -filter -out dbtype -build hg19 -dbtype snp138 snp.avinput /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/humandb/ | Annotate SNPs in dbsnp |
| perl /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/annotate_variation.pl -filter -dbtype 1000g2014oct_all -buildver hg19 -out 1000g snp.avinput /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/humandb/ | Annotate SNPs in 1000 genomes |
| perl /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out Gwas -dbtype gwasCatalog snp.avinput /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/humandb/ | Annotate SNPs in Gwas |
| perl /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/annotate_variation.pl snp.avinput /nfs/srv/databases/annovar/humandb/ -filter -dbtype clinvar_20150629 -buildver hg19 -out Clinvar | Annotate SNPs in Clinvar |
Table 1. Used commands and their description.
Part one. Reads preparation
Amount of reads didn't change dramatically: from 8367 to 8227 (140 were dropped). According to the command was used, reads whose length was less than 50 (after cutting off low quality parts) were dropped.
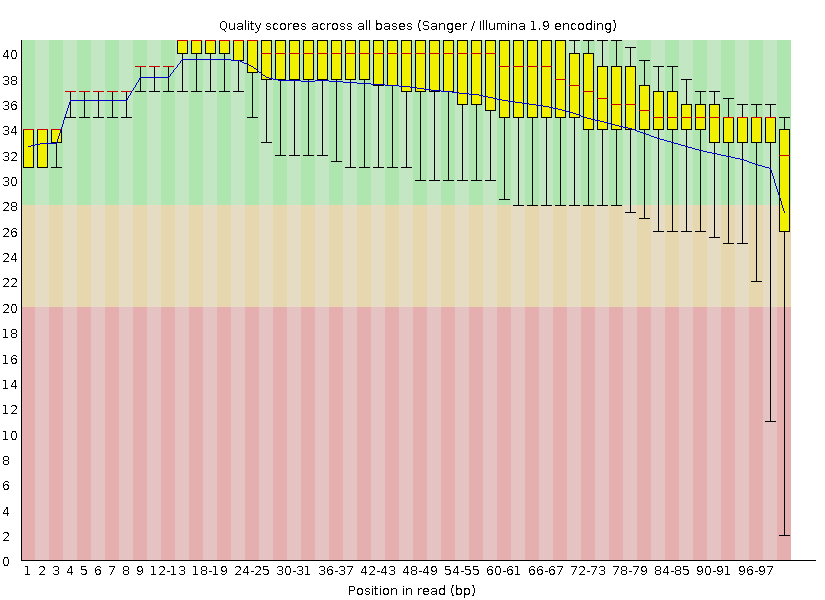
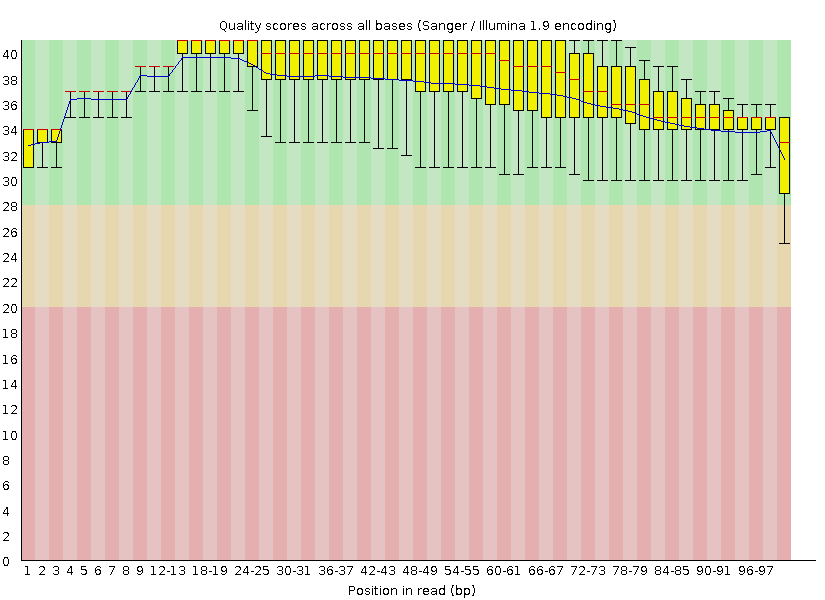
Part two. Reads mapping
Used commands are presented in Table 1. 8227 reads were unpaired, 32 of them were aligned 0 times, 8195 of them were aligned exactly one time (0 were aligned more than once).
8227 reads; of these:
8227 (100.00%) were unpaired; of these:
32 (0.39%) aligned 0 times
8195 (99.61%) aligned exactly 1 time
0 (0.00%) aligned >1 times
99.61% overall alignment ratePart three. SNP analysis
Used commands are presented in Table 1. Examples of polymorphisms are provided in Table 2.
| Coordinate | Polymorphism type | REF/ALT | DP | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27467821 | SNP | C/G | 13 | 149.008 |
| 76402598 | SNP | A/G | 2 | 6.19965 |
| 76453492 | SNP | T/A | 1 | 6.98265 |
Table 2. Examples of polymorphisms.
According to .vcf file 95 SNPs were found, but there were not any indels. Average quality of found SNPs is 66.7, average coverage is 14. Not bad indicators, I suggest. RefGene is dividing SNPs in four categories: intronic, exonic, intergenic, UTR3 and UTR5 (untranslated regions of mRNA 3' and 5' respectively). My ratios: 60 intronic, 5 exonic, 17 intergenic and 13 UTR3. SNPs affected such genes as CLU (Clusterin, Chaperone), HNF4G (Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-gamma, zinc and DNA binding protein, involved in transcription regulation) and TRPS1 (provides instructions for making a protein that regulates the activity of many other genes, interacts with specific regions of DNA to turn off (repress) gene activity). SNPs caused 1 synonymous SNV in CLU gene, 1 synonymous and 2 nonsynonymous SNVs in HNF4G gene and 1 synonymous SNV in TPRS1 gene (list 'SNPs' in excel file). 77 SNPs have rs. The most of SNPs are frequent enough. According to clinical annotation, patient has high risks of Alzheimer's disease and maybe problems with urate levels.