- Jalview pairwise needle sequence alignment (link)
- Download link
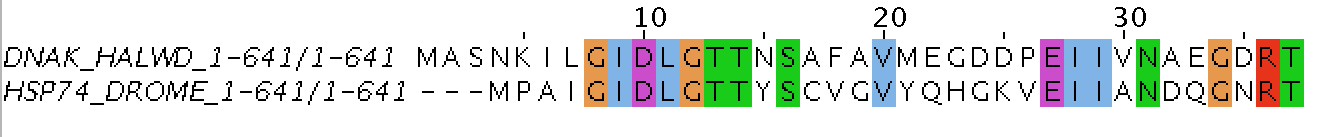
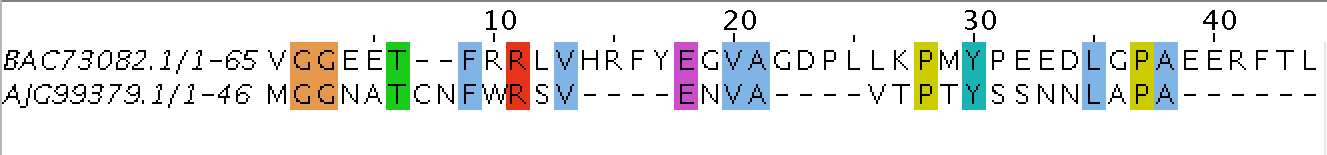
Figure 1. Screenshot of part of the needle alignment
- Jalview pairwise water sequence alignment (link)
- Download link
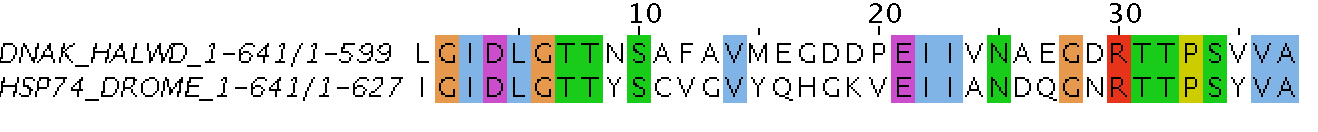
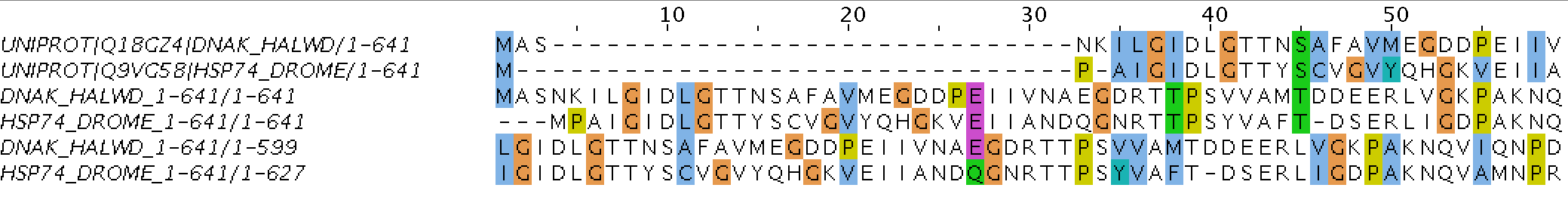
Figure 2. Screenshot of part of the water alignment
Used programs: EMBOSS, Jalview
EMBOSS commands: needle, water
Steps: Input Alignment - From File - file.fasta - Colour - ClustalX - Above Identity Threshold (100%)
Table 1. Main information about chosen proteins
Entry name Length Protein name Organism Phylum DNAK_HALWD
641
Chaperone protein DnaK
Haloquadratum walsbyi (strain DSM 16790 / HBSQ001)
Archaea
HSP74_DROME
641
Major heat shock 70 kDa protein Bbb
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly)
Eukaryota
Table 2. Results of using needle and water EMBOSS commands
| Command | Aligned Length | Indels | Gaps | % (Indels) | Identity | % (Identity) | Similarity | %(Similarity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| needle | 680 | 10/7 | 39/30 | 5.7/4.4 | 641/336 | 94.2/49.4 | 0/109 | 0/16.0 |
| water | 638 | 10/6 | 39/11 | 6.1/1.7 | 599/332 | 93.9/52.0 | 0/108 | 0/16.9 |
Command - displays command (needle - global alignment, water - local alignment);
Aligned length - displays length of alignment;
Indels - displays number of indels - parts of sequence, where insertion or the deletion of bases must have happened[1];
Gaps - dispays number of gaps (group of gaps = indel);
Identity - displays the required number of identities at a position for it to give a consensus;
Similarity - displays a cut-off for the % of positive scoring matches below which there is no consensus.


Table 3. Default data for needle and water EMBOSS commands
| Needle | Water | |
|---|---|---|
| Matrix (for protein sequences) | EBLOSUM62 | EBLOSUM62 |
| Gap open penalty | 10.0 (endopen) | 10.0 (gapopen) |
| Gap length penalty | 0.5 (endextend) | 0.5 (gapextend) |
| Gap end penalty | - (endweight) | - |
Global Sequence Alignment (Needle)
|
Local Sequence Alignment (Water)
|
In global alignment, an attempt is made to align the entire sequence (that's why there are more gaps).
|
Finds local regions with the highest level of similarity between the two sequences (that's why the start of sequences is cut off).
|
A global alignment contains all letters from both the query and target sequences
|
A local alignment aligns a substring of the query sequence to a substring of the target sequence.
|
If two sequences have approximately the same length and are quite similar, they are suitable for global alignment (more suitable for aligning two homological sequences).
|
Any two sequences can be locally aligned as local alignment finds stretches of sequences with high level of matches without considering the alignment of rest of the sequence regions (suitable for aligning more divergent sequences or distantly related sequences).
|
A global alignment technique is the Needleman–Wunsch algorithm.
|
A local alignment method is Smith–Waterman algorithm.
|
Used programs: EMBOSS, Jalview
EMBOSS commands: needle, water
Steps: Input Alignment - From File - file.fasta - Colour - ClustalX - Above Identity Threshold (100%)
Table 4. Water sequence alignment of non-homological sequences (proteins with different functions were taken). All 5 sequences were aligned with my protein, BAC73082.1.
Protein Aligned Length Gaps Indels % (Indels) Identity % (Identity) Similarity %(Similarity) AKC28878.1
32
0/0
0/0
0/0
32/8
100.0/25.0
0/8
0/25.0

AMM47000.1
39
2/0
5/0
12.8/0
34/16
87.2/41.0
0/7
0/17.9
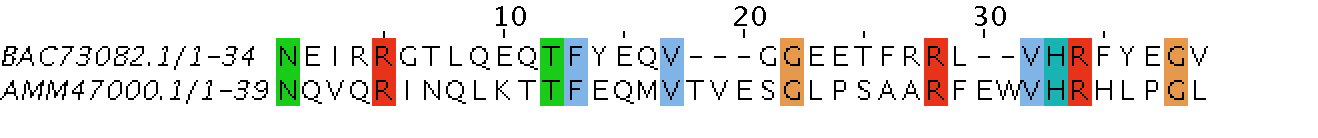
AFH91095.1
140
4/3
26/30
18.6/21.4
114/53
81.4/37.9
0/18
0/12.9
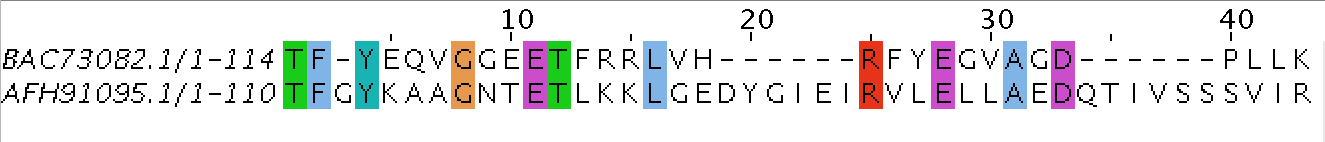
AMD46139.1
53
2/1
6/1
11.3/1.9
47/19
88.7/35.8
0/10
0/18.9
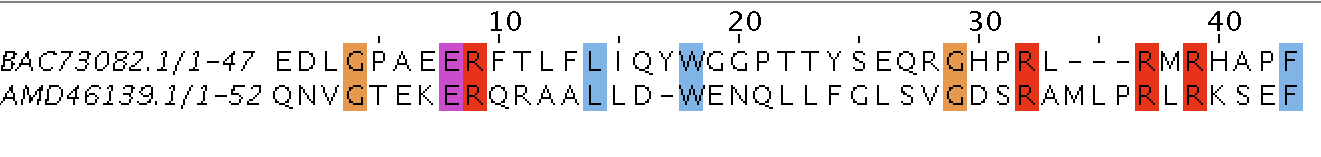
AJG99379.1
67
1/3
2/21
3.0/3.1
65/20
97.0/29.9
0/7
0/10.4