|
In the Table 1 represente main information about bacterial proteomes. It's important to notice that there is U at the E. coli proteome (selenocysteine) |
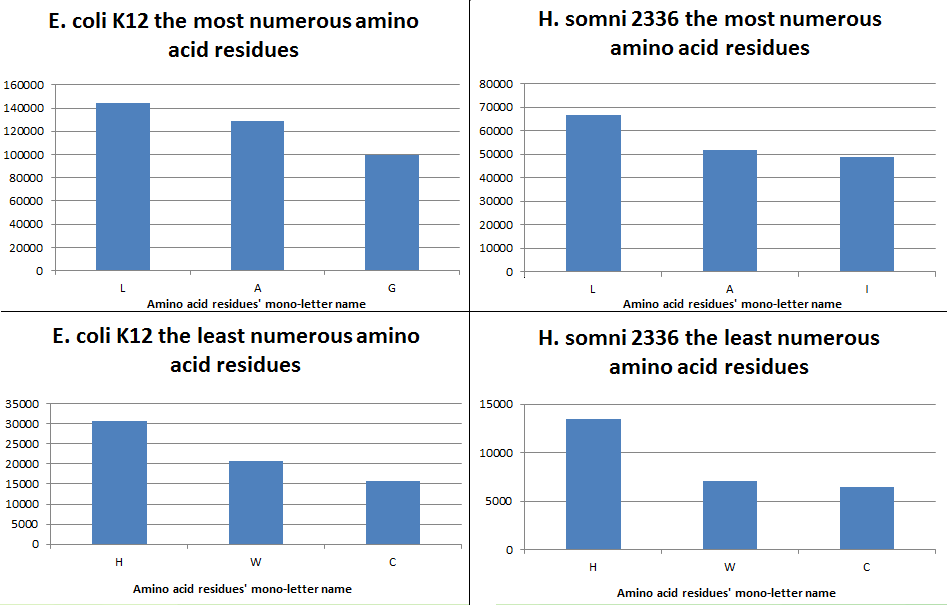
In Table 2, you can see comparative data on the number of amino acid residues in the proteomes of two organisms. You can download Excel table
| Table 2. Amino acid residues' percent-measurements | |||
| Letter | E. coli K12 | H.somni (strain 2336) | Percent difference |
| L | 10,6758 | 10,2033 | 0,4725 |
| A | 9,5115 | 7,9157 | 1,5958 |
| I | 6,0098 | 7,4271 | -1,4173 |
| G | 7,3705 | 6,8218 | 0,5487 |
| K | 4,4057 | 6,7655 | -2,3598 |
| V | 7,0731 | 6,4655 | 0,6076 |
| E | 5,766 | 6,3034 | -0,5374 |
| S | 5,7967 | 6,0956 | -0,2989 |
| T | 5,394 | 5,4432 | -0,0492 |
| N | 3,9369 | 5,1465 | -1,2096 |
| D | 5,1491 | 5,0242 | 0,1249 |
| Q | 4,4434 | 4,8154 | -0,372 |
| F | 3,8927 | 4,2773 | -0,3846 |
| R | 5,5186 | 4,2162 | 1,3024 |
| P | 4,4283 | 3,4624 | 0,9659 |
| Y | 2,8447 | 3,207 | -0,3623 |
| M | 2,8225 | 2,3 | 0,5225 |
| H | 2,2677 | 2,0571 | 0,2106 |
| W | 1,5319 | 1,073 | 0,4589 |
| C | 1,1609 | 0,9798 | 0,1811 |
| U | 0,0002 | 0 | 0,0002 |
|
So, we can say that there are different prevailing amino acids in
E. coli and H. somni proteomes.
In the first and second place Leu (L) and Ala (A) situate;
at the third place we can see Gly (G) (E. coli) or Ile (I) (H.somni)
The rarest amino acids in both organisms are His (H), Trp (W) and Cys (C)
The greatest percentage difference in favor of E. coli: 1,5958 The greatest percentage difference in favor of H. somnie: 2,3598 (-2,3598) |
Small manual and recommendations for users about wordcount and compseq programs
This programs from EMBOSS package count and extract unique words in molecular sequence.
Both wordcount and compseq programs asks user for input filename,
the size of words to count (integer) and the name of output file,
speaking about standard qualifiers
Wordcount program have such option as -mincount (minimum word count to report);
in other words, if the number of counted words is less then you pointed at the -mincount option,
this word won't be written to the output file.
It's very convenience if you want to find words with a certain frequency.
Wordcount's output file looks like two columns separated by a tabulator.
At the first column you can find words' variant; at the second words' frequency pointed
Compseq program has a lot of additional options. There're -infile, -frame
("this option allows you to move the window up by the length of the word each time,
skipping over the intervening words" - from official user's manual);
boolean: -[no]ignorebz, -reverse,
-calcfreq, -[no]zerocount.
Compseq's output file looks like four columns separated by a tabulator.
Here they are: selected words, words' frequency (real),
words' frequency (expected), real and expected frequences ratio.
So, compseq gives you wider information about word's frequency.
But if you don't need so many data for your work,
it's easier to work, using wordcount program.
Use compseq for more complicated and extensive tasks