|
|
|
- Task 1: For the task, I worked with the protein with Uniprot ID P74325.
- Its only domain is S6PP (the final stage of sucrose synthesis, that is, the hydrolysis of the phosphoether bond) with ID PF05116. A link to a list of all domain architectures. I have chosen the S6PP architecture with 388 representatives (code A) and Sucrose_synth, Glycos_transf_1, S6PP (code B) with 270 representatives. The Sucrose_synth domain is involved in the synthesis of sucrose from D-fructose and glucose activated by nucleotide diphosphate. The domain Glycos_transf_1 is a variant of domains found in glycosyltransferases. The taxa under investigation are the domain of bacteria and the kingdom of proteobacteria (code P) and cyanobacteria (code C). The alignment of the selected proteins with these two domain architectures from these two taxa was performed. The materials involved: spreadsheet and project with alignments.
Evolutionary tree:
- A tree was constructed from the selected proteins by the method of greatest similarity. The tree received is presented below. Its bracket form is available by reference. According to this tree, it is clear that the domain in a complex protein is more conservative than in a single protein, since interactions with other domains impose a stronger stabilizing selection on the structure. Such domains are compactly allocated for the same reason (green). There is no serious division by taxa, and it can not be explained only by the horizontal transfer of genes.
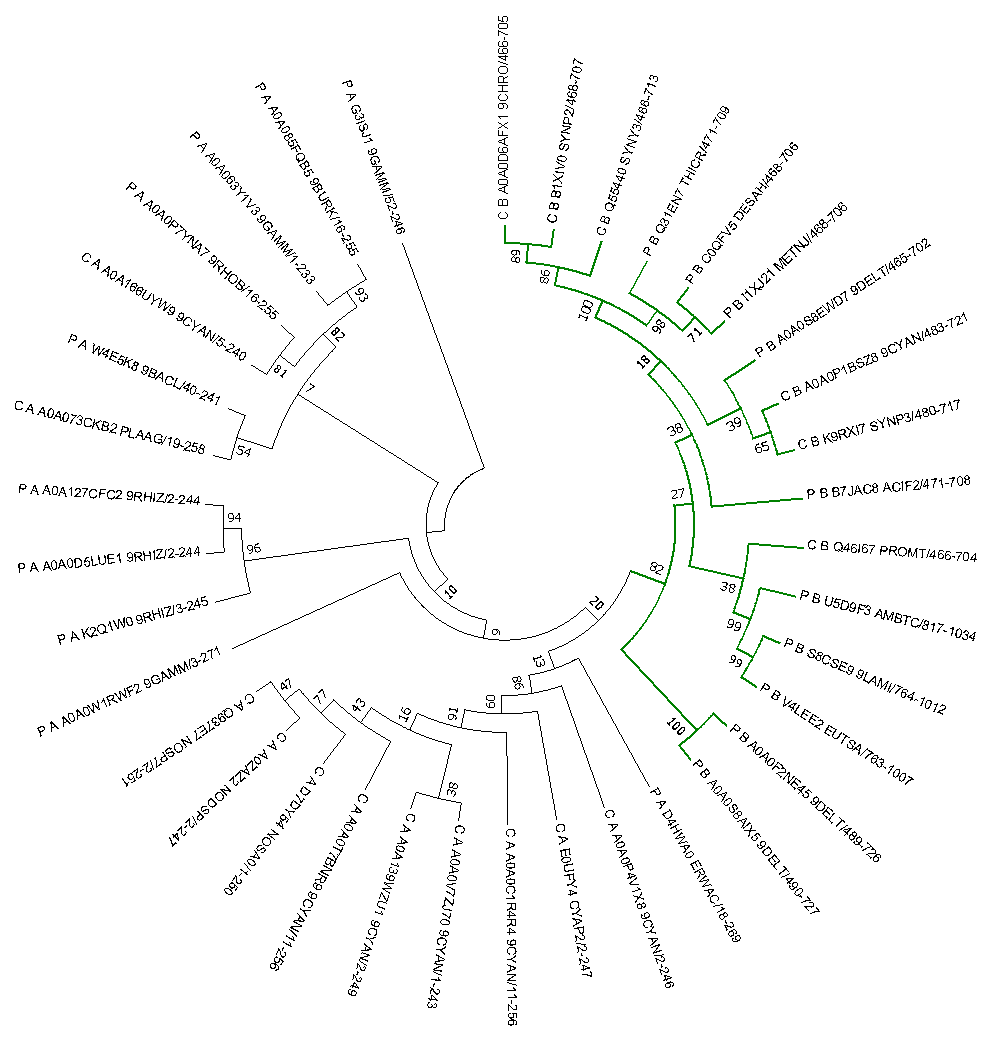
|
|
|
|