|
|
|
General information about the metabolic pathway of lysine biosynthesis:- Amino acid lysine biosynthesis scheme (Path ID in the KEGG database - map00300):
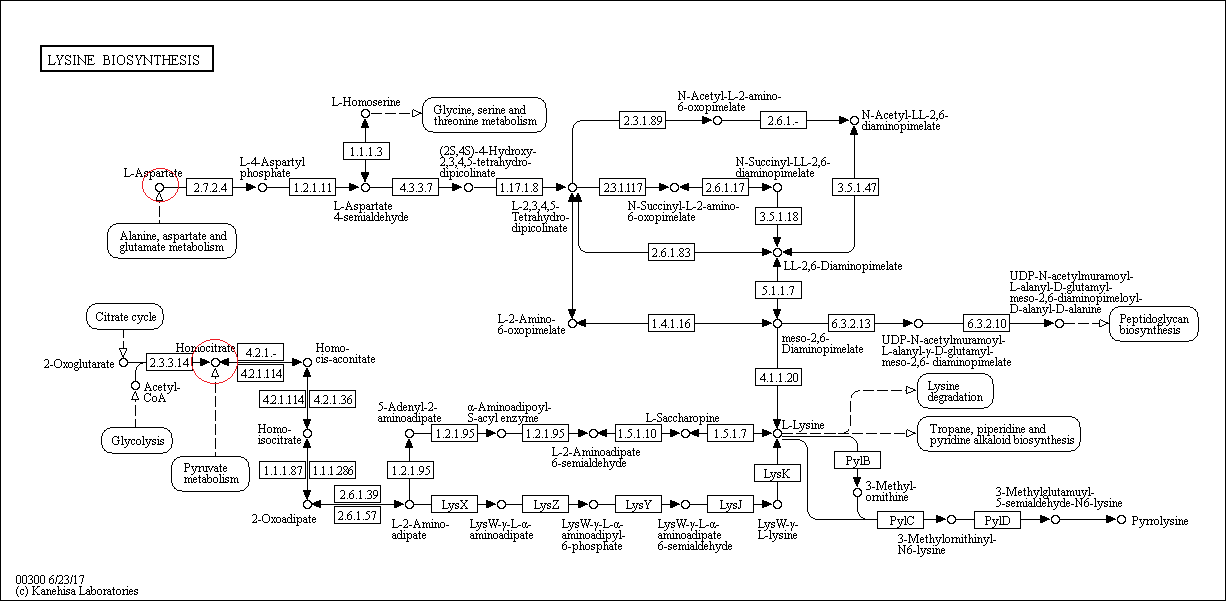
- Lysine is an essential amino acid. In plants and most bacteria, synthesis begins with aspartate; fungi, euglenoids and some prokaryotes produce lysine via the alpha-amino-adipate pathway. According to the scheme from KEGG from lysine in several stages it is possible to obtain non-standard amino acid pyrrolizine. In addition, the synthesis of proteoglycan is close to the scheme.
- Lysine biosynthesis is associated with glycolysis, the cycle of tricarboxylic acids and the metabolism of pyruvate through homocitrate. On the other hand, with the synthesis of lysine, the metabolism of alanine, aspartate and glutamate (via L-aspartate) is knitted. Lysine biosynthesis is also associated with the metabolism of glycine, serine and threonine (via L-homoserine.) The linking compounds on the diagram are marked with red circles.
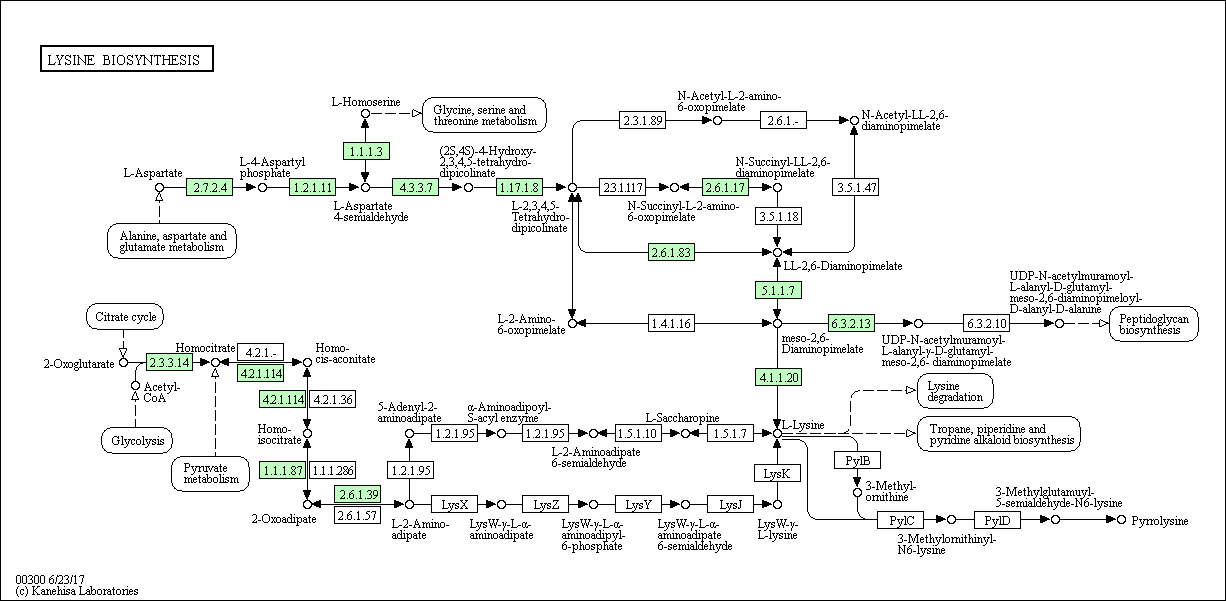
The metabolic pathway of lysine biosynthesis in different domains of life:- Lysine biosynthesis scheme for Methanobacterium paludis (Taxonomy: Kingdom: Archaea
Phylum: Euryarchaeota
Subphylum: Methanobacteria
Order: Methanobacteriales
Family: Methanobacteriaceae
Genus: Methanobacterium
Species: Methanobacterium paludis)
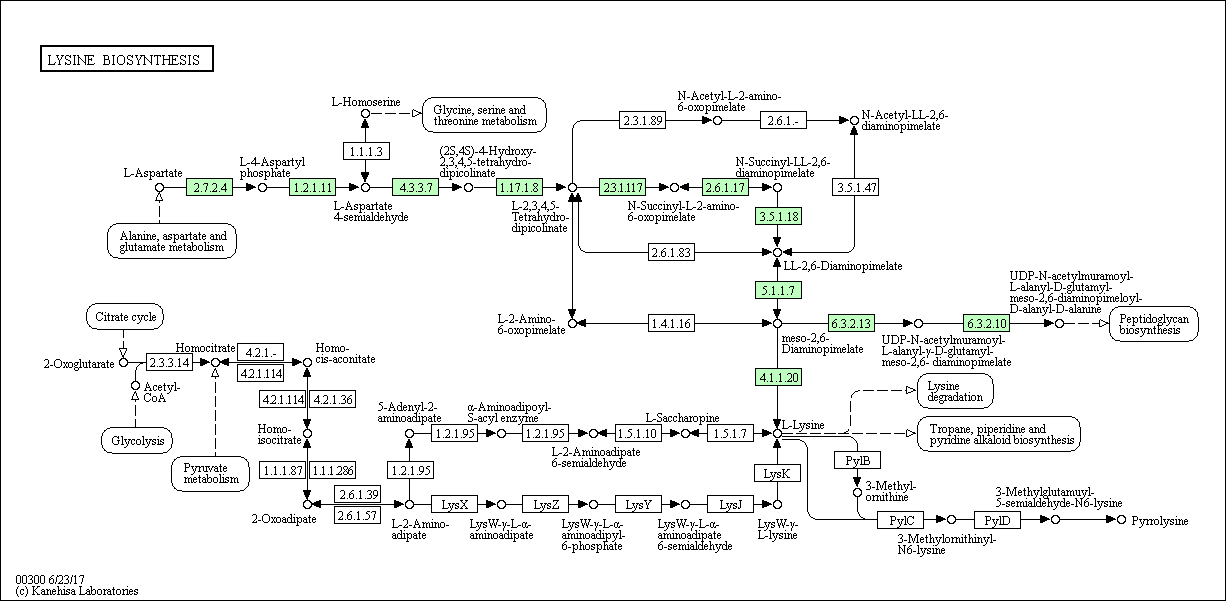
- Lysine biosynthesis scheme for Tatlockia micdadei (Taxonomy: Kingdom: Bacteria
Phylum: Proteobacteria
Subphylum: Gammaproteobacteria
Order: Legionellales
Family: Legionellaceae
Genus: Tatlockia
Species: Tatlockia micdadei)
- Lysine biosynthesis scheme for Cucumis sativus (Taxonomy: Kingdom: Plantae
Clade: Angiosperms
Clade: Eudicots
Clade: Rosids
Order: Cucurbitales
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Genus: Cucumis
Species: Cucumis sativus)
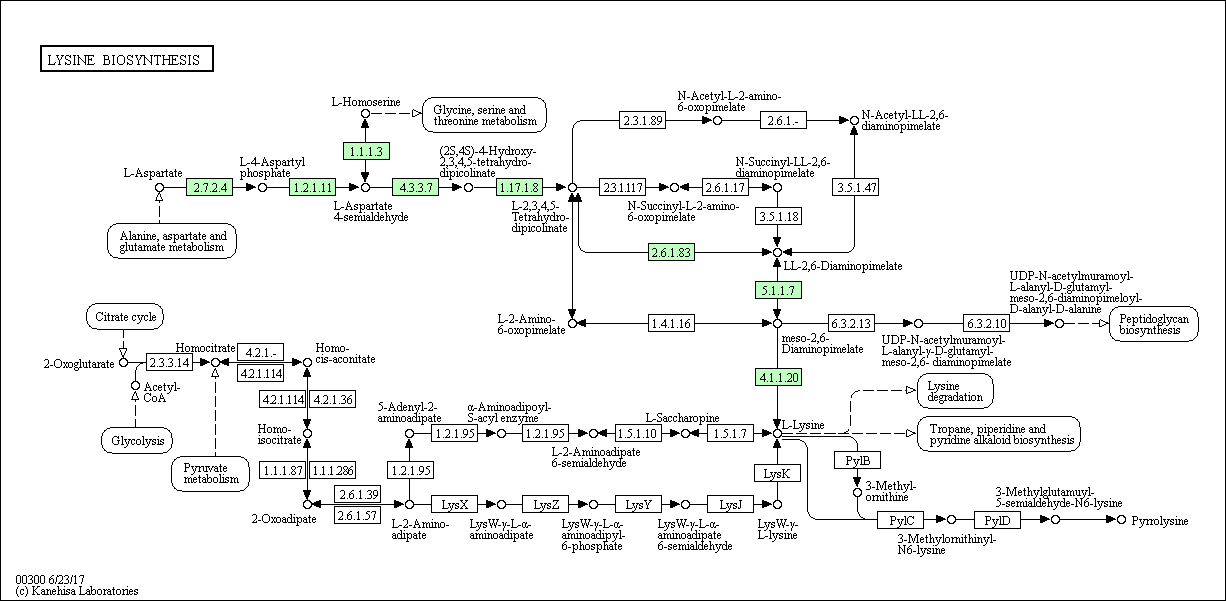
- Part of the diaminopimeline pathway in which from aspartate by successive transformations involving enzymes 2.7.2.4, 1.2.1.11, 4.3.3.7, 1.17.1.8, leading to the formation of L-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate, is present in all three taxa . And also the way of obtaining lysine from LL-2,6-diaminopimelate by the action of enzymes 5.1.1.7 and 4.1.1.20 is present in three taxa. From which we can conclude that these paths are important for the normal life of organisms in these taxa. Separately, for each selected organin, one can say that they all synthesize lysine from aspartate, but the archaea perform part of the pathway for the synthesis of L-2-aminoadipate by using a substrate from the Krebs cycle, but no other taxa of this region are observed. It is quite natural that for the bacterium there is a link with the way of obtaining peptidoglycans, and there are enzymes providing this connection - 6.3.2.13 and 6.3.2.10.
Reaction R09775 in the KEGG database:- This reaction of the pathway of lysine biosynthesis is presented below:

|
|
|
|