Serratia proteamaculans
Taxonomy
|
| Microphotography S.proteamaculans |
cellular organisms
domain Bacteria
group Proteobacteria
class Gammaproteobacteria
order Enterobacteriales
family Enterobacteriaceae
genus Serratia
species Serratia proteamaculans
Description
Serratia proteamaculans is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium.
Serratia proteamaculans 568, an Enterobacteriaceae, was isolated as a root endophyte from
Populus trichocarpa. S.proteamaculans has been found promote plant growth, and it has been
demonstrated that this occurs via the production of specific compounds, such as lipo-chitin
oligosaccharides, which are used as specific bacteria-to-plant signals. Individual plant growth
promoting bacteria produce specific structurally diverse LCO mixtures. Endophytes are bacteria
that live within the tissue of a plant without substantively harming it. They can help promote
plant growth in several ways, including helping the host overcome toxic effects of environmental
pollution.
The sequencing of S. proteamaculans 568 genome provided an ideal
basis to study bacteria to plant signaling of this bacterium and its poplar host
Chitinases of Serratia proteamaculans
Serratia proteamaculans 568 genome revealed the presence of four family 18 chitinases (Sp ChiA, Sp ChiB, Sp ChiC, and Sp ChiD). Heterologous expression and characterization of Sp ChiA, Sp ChiB, and Sp ChiC showed that these enzymes were optimally active at pH 6.0-7.0, and 40°C. The three Sp chitinases displayed highest activity/binding to ß- chitin and showed broad range of substrate specificities, and released dimer as major end product from oligomeric and polymeric substrates. Longer incubation was required for hydrolysis of trimer for the three Sp chitinases. The three Sp chitinases released up to tetramers from colloidal chitin substrate. Sp ChiA and Sp ChiB were processive chitinases, while Sp ChiC was a non-processive chitinase. Based on the known structures of ChiA and ChiB from S. marcescens, 3D models of Sp ChiA and Sp ChiB were generated.Genome and proteome
Serratia proteamaculans has one chromosome and one plasmid (see table 1 for characteristics).
| Table 1 | |||||||
| Component name | Protein count | Type | Length (bp) | Av. CDS Length | GC content | CDS coverage | Gene count |
| Chromosome | 4891 | ring | 5448853 | 972.086 | 55.1% | 87% | 4891 |
| Plasmid pSPRO01 | 51 | ring | 46804 | 677.176 | 49.2% | 74% | 51 |
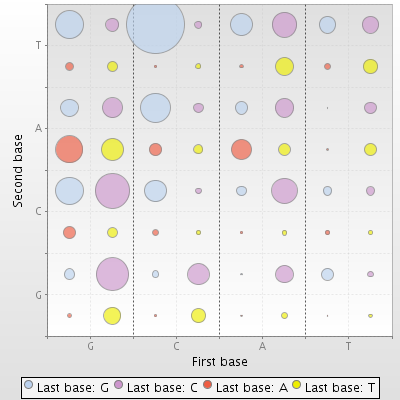
The most usable codon in chromosome is CTG, in plasmid it is GAA. You can find full information in diagrams 1 and 2.
|

|
| Diagram 1. Triplet usage in chromosome | Diagram 2. Triplet usage in plasmid |
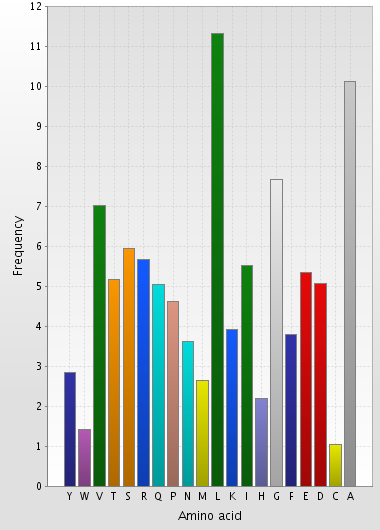
The most widespread aminoacid in proteins of S. proteamaculans is leucine, alanine and glycine (diagram 3). Most proteins are composed of 100-500 amino-acids (diagram 4).
 |
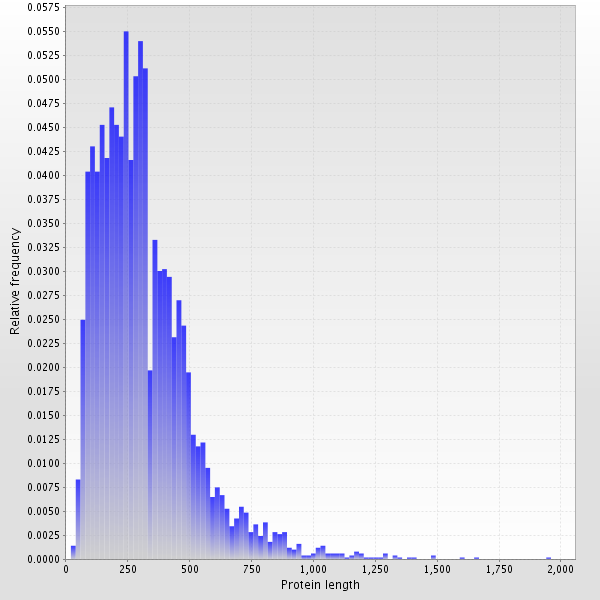 |
| Diagram 3. Amino acid composition | Diagram 4. Protein length distribution |
Sources
- Taxonomy - UniProt
- Microphotography - DOE Joint Genome Institute
- Description - Integr8 : S.proteamaculans
- Chitinases - article "Multiple chitinases of an endophytic Serratia proteamaculans 568 generate chitin oligomers", authors: Purushotham P, Sarma PV, Podile AR. PubMed ID:22406064
database query "Serratia proteamaculans [TI] AND genome". Original abstract
