Bacterium Streptobacillus moniliformis
Taxonomy[1]
| -Cellular organisms | ||
| Superkingdom | -Bacteria (eubacteria) | |
| Class | - Fusobacteriia | |
| Order | - Fusobacteriales | |
| Family | - Leptotrichiaceae | |
| Genus | - Streptobacillus | |
| Species | - Streptobacillus moniliformis |
Proteome and genome of the bacteria [2]
- Protein count – 1423
- Chromosome type – circular
- Length – 1662578 bp
- Av. CDS Length – 1017.107
- GC content – 26,3%
- CDS coverage – 88%
- Gene count – 1434
Relevance of genome sequencing [3]
This organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of its phylogenetic position (scheme 1), and is part of the «Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea»:
Description of the bacterium [3]
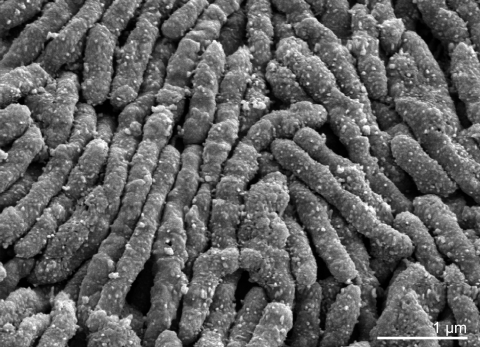 Fig.1 Electron micrograph of S. moniliformis 9901T [3]
Fig.1 Electron micrograph of S. moniliformis 9901T [3]Streptobacillus moniliformis (fig.1) is the type and sole species of the genus Streptobacillus and is of phylogenetic interest because of its isolated location in the sparsely populated. S. Moniliformis is a Gram-negative (fig (2)), non-motile, pleomorphic, fastidious, slow-growing anaerobic organism. It grows as elongated rods (from 0.3-0.7 µm to 1-5 µm in length) which tend to form chains or filaments. The primary habitat of S. moniliformis is small rodents, including rats (dominant reservoir) and more rarely gerbils, squirrels and mice. (is the part of the nasopharyngeal microbiota of rodents [4]). Rat-eating carnivores such as dogs, cats, ferrets and pigs can also become hosts and thus transfer the pathogen to humans (show in the form of rat-bite fever [4]). However, the organism is not directly transmitted from person to person and thus presents a typical zoonotic agent.
Working article [3]
«Complete genome sequence of Streptobacillus moniliformis type strain (9901T)»
Published online 2009 December 30.
Authors
Nolan M, Gronow S, Lapidus A, Ivanova N, Copeland A, Lucas S, Del Rio TG, Chen F, Tice H, Pitluck S, Cheng JF, Sims D, Meincke L, Bruce D, Goodwin L, Brettin T, Han C, Detter JC, Ovchinikova G, Pati A, Mavromatis K, Mikhailova N, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Land M, Hauser L, Chang YJ, Jeffries CD, Rohde M, Spröer C, Göker M, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Kyrpides NC, Klenk HP, Chain P.
PubMed ID: 21304670
Abstract
Streptobacillus moniliformis Levaditi et al. 1925 is the type and sole species of the genus Streptobacillus, and is of phylogenetic interest because of its isolated location in the sparsely populated and neither taxonomically nor genomically much accessed family 'Leptotrichiaceae' within the phylum Fusobacteria. The 'Leptotrichiaceae' have not been well characterized, genomically or taxonomically. S. moniliformis,is a Gram-negative, non-motile, pleomorphic bacterium and is the etiologic agent of rat bite fever and Haverhill fever. Strain 9901T, the type strain of the species, was isolated from a patient with rat bite fever. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. This is only the second completed genome sequence of the order Fusobacteriales and no more than the third sequence from the phylum Fusobacteria. The 1,662,578 bp long chromosome and the 10,702 bp plasmid with a total of 1511 protein-coding and 55 RNA genes are part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Articles search was performed using the query (Streptobacillus moniliformis) and (2000:2012[DP])
Number of results – 54
{if don't limit the time when the article was published – 179}
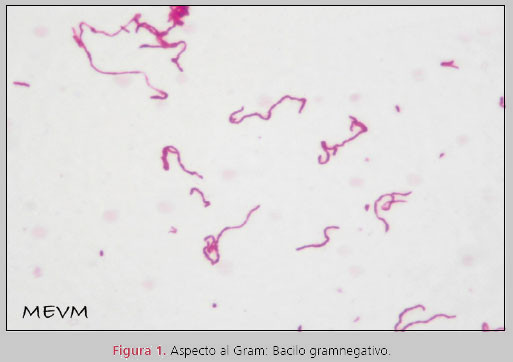
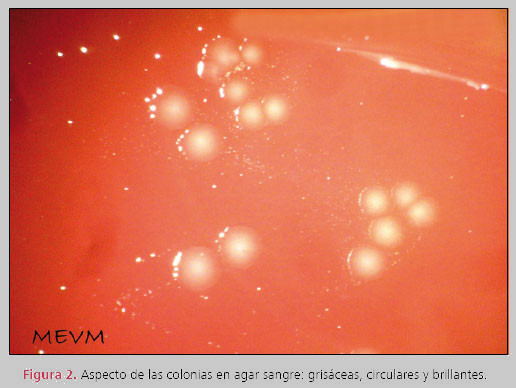
| Fig (2): Look at Gram: Bacteria is Gram-negative | Appearance of colonies on blood agar: gray, circular and bright |


